-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
粘膜支持による可撤式総義歯
Key points
- 天然歯と比較し、無歯顎の歯槽堤は支持の質・量とも劣るため、残遺歯槽堤の縮小(RRR)が起こりやすくなります。
- 義歯を支える粘膜、粘膜下層、下にある歯槽骨による支持には、経時的な適応能力および義歯の動きに対する許容性に対して限度があります。
- 義歯の緩みは、機能低下(発話、咀嚼)とともに、義歯性口内炎、カンジダ感染症、刺激性粘膜過形成(irritation hyperplasia)、フラビーガムその他、様々な臨床症状につながる可能性があります。
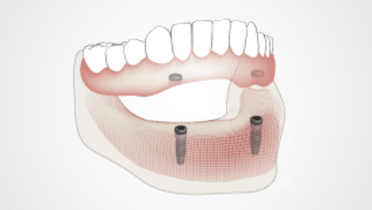
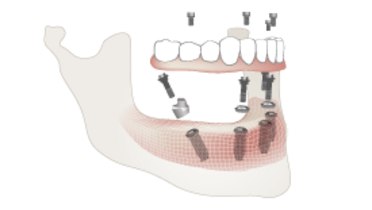
- 総義歯で容認できるQOLが達成されない患者については、口腔インプラント治療を真剣に検討します。
総義歯による治療
研究および臨床経験は、従来型の総義歯が大部分の無歯顎者にとって使用に耐えられることを示しています。総義歯に満足している患者は自らの義歯体験にうまく適応し、義歯を使って食事や会話をすることを学んでいます。義歯装着体験の最良の予後には、吸収が最小限の健康な顎堤、うまく設計された咬合が含まれると考えられています。しかし、最適に作られた従来型の総義歯は、無歯顎に対する万能の治療法ではありません。多数の患者は義歯が不適であり、総義歯装着への適応に苦労し、自らのQOLが低下したと見なしているのです。
総義歯-機能に関する注意事項
従来型の総義歯の土台は、床下部の粘膜、粘膜下層、歯槽骨です。これらの組織はすべて、適応能力が限られており、歯と歯周靱帯、またはオッセオインテグレーテッド口腔インプラントがもたらす水準の機能を提供することはできません。口内の筋肉、特に舌の活動は義歯の緩みにつながり、患者の発話および咀嚼能力を損なう可能性があります。重度の顎堤吸収は、平坦な義歯支持領域を特徴とします。こうした状況では、義歯は水平方向に自由に滑ります。QOLに関し満足のいく対応が困難な場合、口腔インプラントによる固定源を用いた義歯の保定・安定向上の適応となります。総義歯を装着することが困難だった患者については、インプラントオーバーデンチャーまたは固定式インプラント補綴物により、歯槽骨および機能効率への経時的変化の影響を大幅に減少させることができます。
臨床トピック
Related articles
Questions
ログインまたはご登録してコメントを投稿してください。
質問する
ログインまたは、無料でご登録して続行してください
You have reached the limit of content accessible without log in or this content requires log in. Log in or sign up now to get unlimited access to all FOR online resources.
FORウェブサイトにご登録していただきますと、すべてのオンライン・リソースに無制限にアクセスできます。FORウェブサイトへのご登録は無料となっております。