-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
CT
Key points
- スパイラルマルチスライスCTは、最良の画質を提供します。
- 補助的パノラマ撮影および口内法X線撮影は不要です。
- 定量的CTは骨密度を測定することができます。
- 治療計画作成時は測定誤差を考慮に入れる必要があります。
CT – 概論
断層撮影は、物体のスライスの2次元画像を作成します。コンピュータ断層撮影(CT)は、仮想スライスを作成することができます。従来のCTは1スライス撮影毎に寝台が移動し、停止します。スパイラル/ヘリカルCTは、らせん状に連続的なスキャニングを行うため、高速で連続した画像を獲得することができます。
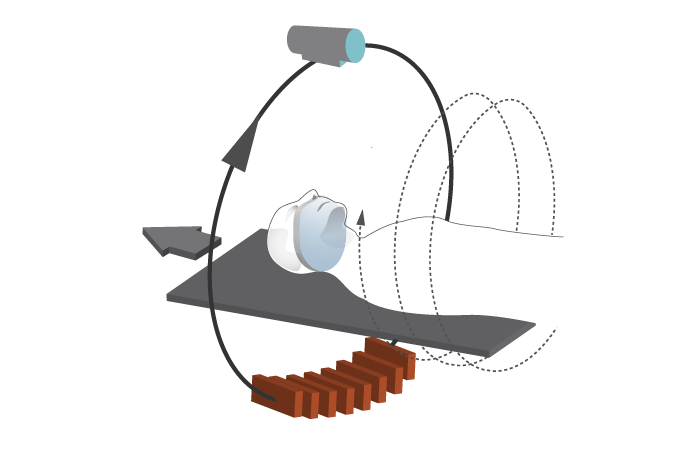
現在では、分解能<0.5mmを実現した64列マルチスライスCTスキャナーが販売されています。また、CT画像の適用可能性と効率を高めるため、口腔および上顎の画像を再構成するための専用のソフトウェアプログラムも販売されています。CATの「A」は体軸面(axial plane)を指していますが、冠状面や矢状面といった他の断面も獲得することができます。
解剖学的距離と骨量/密度の計算
下顎管までの距離、骨高径および骨幅の測定には、過大評価≤ 1.1 mm、過小評価≤1.4 mmの誤差が生じます。このため、骨切り術の準備やインプラントのポジショニングのための治療計画作成時には、これらの数値の最大値(「安全領域」)を考慮に入れる必要があります。
CTスキャンにより獲得したデジタルデータはピクセルおよびボクセルにより構成され、3次元の断面図として表示されますので、骨量および骨密度を算出することができます。
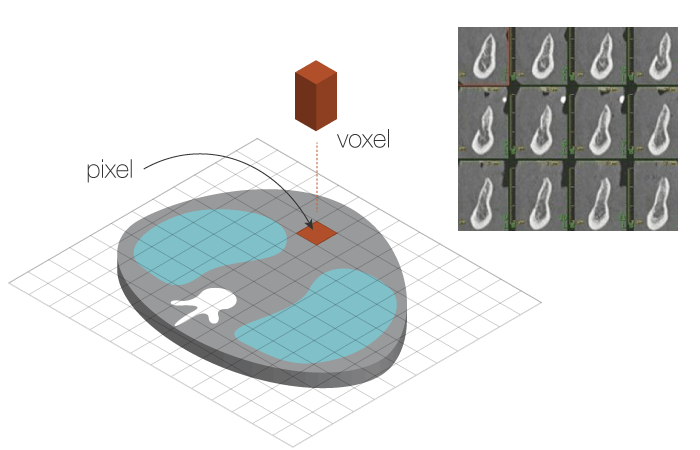
CTから算出された密度はハウンスフィールド単位(HU)で表示されます。組織の種類および上顎-下顎の部位によるHU値は次の通りです。
- 空気 = -1000
- 脂肪 = - 80~-100
- 水 = 0
- 軟組織 = 10~80
- 骨 = 400~3000
- 上顎皮質骨 = 800~950
- 上顎結節皮質骨 = 450~615
- 下顎皮質骨 = 800~1600
- 下顎歯槽骨 = 1300
- 下顎骨基底部 = 1500
定量的CT(QCT)は、骨密度の基準となるファントムとともに身体をスキャニングし、HUを骨密度値に変換します。感度は単一光子吸収法の3~4倍、二重光子吸収法の2倍以上ですが、精度は後者に劣ります。