-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
CT
Key points
- 螺旋多层 CT 可提供最佳图像质量
- 没有必要采用辅助全景和口腔内 X 光片
- 通过定量 CT 可以测量骨密度
- 在治疗方案设计中,必须考虑到测量误差
CT - 简介
X 线断层摄影术可呈现贯穿物体的断层的 2-D 图像。计算机辅助 X 线断层摄影术 (CT) 可产生虚拟断层,而传统 CT 是逐层扫描,机器在断层间停止和移动。螺旋/螺旋状 CT 则是以螺旋方式连续扫描,从而更快地产生连续图像。
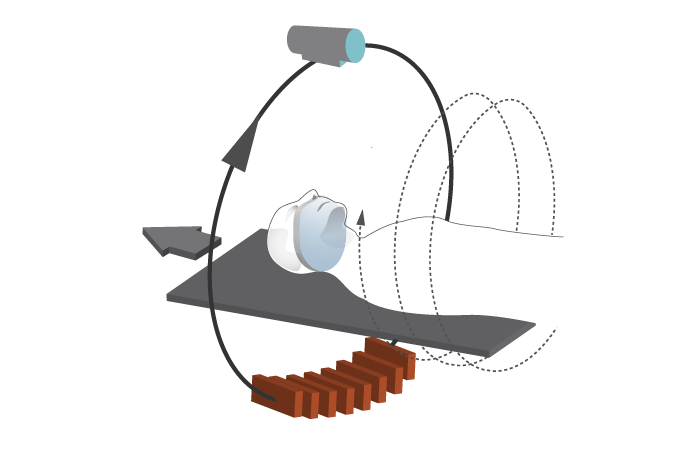
64 层扫描仪可实现 < 0.5 毫米的分辨率,适用于口腔和上颌图像重建的特定软件程序可提高 CT 成像的效率和适用性。CAT 中的“A”是指轴向平面,但也可以获得冠状或矢状等其他平面。
解剖距离和骨体积/密度计算
到下颌管的距离、总骨高度和骨宽度都可能产生测量误差。高估 ≤ 1.1 毫米,低估 ≤1.4 毫米。因此,在进行骨凿准备和种植体定位的治疗方案设计时,必须将这些最大值考虑在内(“安全区域”)。
CT 扫描产生的数字数据由像素和体素组成,以 3-D 横截面图片形式显示。 因此,可以计算骨体积和密度。
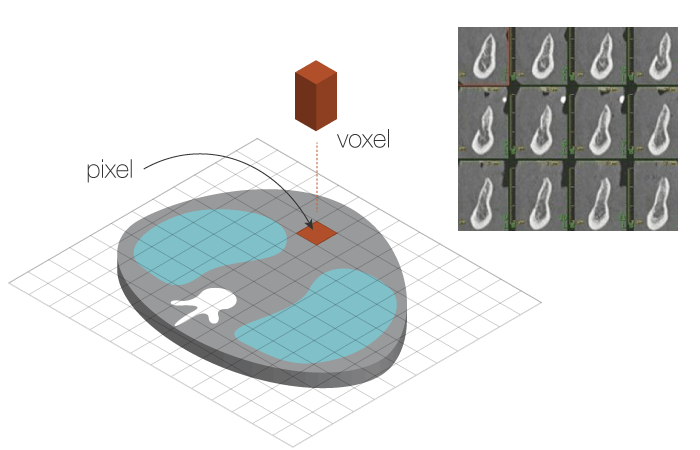
通过 CT 计算得到的密度以亨氏单位 (HU) 表示,下面列出的是不同组织类型及上下颌部位的密度。
- 空气 = -1000
- 脂肪 = - 80 到 -100
- 水 = 0
- 软组织 = 10 到 80
- 骨 = 400 到 3000。
- 上颌皮质骨 = 800 - 950
- 上颌结节皮质骨 = 450 – 615
- 下颌皮质骨 = 800 - 1600
- 下颌牙槽骨 = 1300
- 下颌基骨 = 1500。
定量 CT (QCT) 需要插入被扫描体的校准标准,以便将 HU 转换为骨矿物质密度值。灵敏度高出单光子吸收法 3-4 倍,高出双光子吸收法 2 倍。精度低于后者。




