-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
BRONJ / ARONJ
Key points
- 服用双磷酸盐药物 (BP) 可导致“与双磷酸盐药物相关的颌骨骨坏死”(BRONJ)
- BRONJ 与骨坏死相似,通常表现为口腔内骨骼裸露
- BRONJ 难以治疗。如果患者被诊断为 BRONJ,必须听从牙科和医学康复团队的建议并密切配合
- 术语 ARONJ(与骨吸收抑制药相关的颌骨骨坏死)现在替代了术语 BRONJ
一般注意事项
长期服用、特别是静脉注射双磷酸盐药物的患者如果观察到口腔颌面部区域发生严重副作用,会导致“与双磷酸盐药物相关的颌骨骨坏死”(BRONJ) 或者“与骨吸收抑制药相关的颌骨骨坏死”(ARONJ)。根据定义,这是连续服用双磷酸盐药物 8 周以上且无放射治疗史的患者出现的颌骨裸露区域。
采用双磷酸盐药物治疗骨质疏松症和帕哲氏病引发 BRONJ 的机率为 0.01% - 0.04%。采用双磷酸盐药物治疗骨癌和骨转移引发 BRONJ 的机率为 0.8% - 12%。
与双磷酸盐药物相关的颌骨骨坏死与放射性骨坏死相似,很难治疗。受影响骨骼的愈合能力下降(恢复速度减慢),并且血管生成减慢。导致抗感染和外伤(手术、拔牙)愈合能力下降。
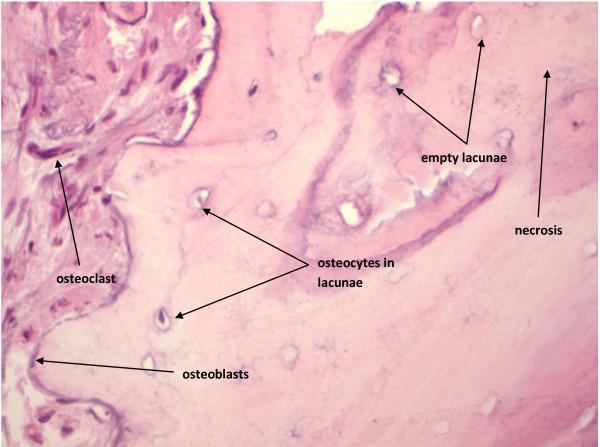
BRONJ 治疗考虑事项
如果患者诊断为 BRONJ,应避免手术和拔牙。应重新评估并加强卫生措施。这种情况需要全科医生、内科医生、牙医及口腔颌面外科医生定期沟通并开展团队合作。
已制定出详尽全面的双磷酸盐药物患者管理临床实践指南。要使用的一些基础治疗步骤包括:
- 日常冲洗和抗菌冲洗
- 抗生素抑制感染
- 针对复杂病例建议通过手术治疗切除坏死骨骼
- 对于某些患者,需要使用活动矫正器覆盖并保护裸露骨骼
- 保护性支架会损坏周围软组织或破坏正常功能
- 如果义齿有磨损,应尽量减少对软组织的刺激,对于接受双磷酸盐药物 IV 治疗的患者尤其如此。晚上应摘下义齿并彻底清洁。
(Content © Copyright AAOMS 2008-2013)