-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
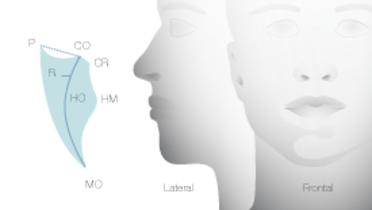
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
咬合
Key points
- 咬合包括各种形态和功能变化,功能方面被视为生理性咬合的适当决定因素
- 咀嚼系统能够在功能上很好地适应各种咬合形态差异
- 使用全口义齿治疗缺齿患者时,大多数牙齿排列和咬合问题都很容易解决
- 在缺齿牙颌存在大小差异的情况下设计种植体治疗方案时,则需要进行严谨的临床分析,以确保获得最佳咬合和美齿效果
咬合 - 简介
理想的咬合一直很难有普遍接受的定义。这是因为理想的咬合只能从各种生理形态和功能的广义角度来定义。在预期的人类多样性的大背景下,咬合的功能方面(而不是特定的解剖牙齿关系和位置)现在被视为生理性咬合的适当决定因素。这也是因为在实践中和报道中有相当多样的解剖和牙科差异,它们很少会导致咀嚼功能障碍。除非其特征是牙槽嵴大小、形态和牙齿排列存在严重不协调,否则这些差异很少需要治疗。咀嚼系统的功能适应性能够很好地应对各种与所谓“正常”咬合形态的偏离。
咬合与面容
不过,齿系对人的面容起着毋庸置疑的作用,因为其形态、位置和牙弓关系可以改善也可以损害任何人的外貌。这些差异包括大多数人的主观审美观念,在年龄、性别、整体面部特征甚至个性等考虑因素的背景下,还受到文化和社会决定因素的影响。
因此,不同程度的深覆和覆盖,或牙弓形态和唇齿关系等问题,可能会被视为设法通过矫正或修复治疗来纠正咬合(较少通过正颌外科矫治)的令人信服的理由。
咬合与种植体治疗
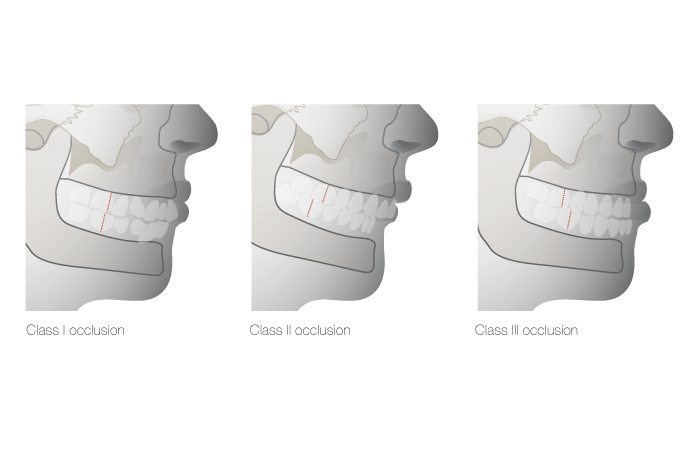
使用全口义齿治疗缺齿患者时,大多数牙齿排列和咬合问题都很容易解决。不过,在缺齿牙颌存在大小差异(所谓的安氏 II 类 1 分类和 III 类牙颌形态)的情况下设计种植体治疗方案时,则需要进行严谨的咬合诊断模型分析,以协调获得最佳功能和美齿效果所需的手术和修复方案。与固定修复体相比,种植体上的覆盖义齿可能更容易解决此类牙弓大小和咬合差异。特定的种植体角度、使用斜角式基台以及旨在“矫正”上层覆盖义齿的杆卡设计,可能也有助于提高设计灵活性。