-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
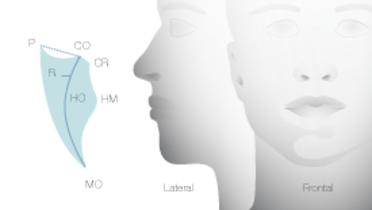
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
無歯顎の骨への影響
Key points
- 上顎歯列全体を除去した後、歯槽頂部は上方内側へ吸収されます。
- 対照的に、下顎の歯槽頂部は下方外側へ吸収されます。
- その結果生じる上顎-下顎の関係は、顔貌の悪化、咬合の不安定、補綴物の機能低下を招く可能性があります。
上顎歯槽堤吸収/縮小
上顎の骨吸収は、特に前部で残遺歯槽堤/歯槽の吸収を引き起こしますが、これは唇側に広がります。この吸収の結果、上顎の歯槽頂部が徐々に内側または口蓋へ移動します。その結果、上顎の唇支持が低下し、顔面形態に変化が起こります。特に、可撤式または固定式義歯で十分に補わない場合、「くぼんだ顔(“sunken face”)」になります。また、これにより、義歯が歯槽堤頂部唇側に位置することになるため、義歯の咬合関係悪化をも招く可能性があります。
下顎歯槽堤の吸収/縮小
下顎の骨吸収は、上顎の場合とは異なる歯槽堤吸収過程を生じます。下顎の舌側の傾きが徐々に歯槽堤頂部の下外側への移動を生みます。
上顎-下顎の関係
上顎は上方後部へ吸収し、下顎は下方前部へと、両者は前後方向に吸収されます。上顎および下顎の両方で中等度から重度の歯槽堤吸収を経験した患者では、結果として起こる骨のクラスIII(下顎前突の外観)の関係が生じます。補綴学の原則では、義歯を残遺歯槽堤頂部でなく、筋肉のニュートラルゾーン(muscular neutral zone)に設定することを支持しています。総義歯およびオーバーデンチャー等、組織の支持が必要な場合、前歯部の配列はエンドツーエンドの関係に、臼歯部の配列は反対咬合(交差咬合)の関係に配置する必要がある場合があると考えられます。歯の位置に関する最終決定は、患者の願望を審美的にも機能的にも満たす必要があります。
臨床トピック
Related articles
Questions
ログインまたはご登録してコメントを投稿してください。
質問する
ログインまたは、無料でご登録して続行してください
You have reached the limit of content accessible without log in or this content requires log in. Log in or sign up now to get unlimited access to all FOR online resources.
FORウェブサイトにご登録していただきますと、すべてのオンライン・リソースに無制限にアクセスできます。FORウェブサイトへのご登録は無料となっております。