-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
粘膜支撑活动全口义齿
Key points
- 与天然牙相比,缺齿牙槽牙嵴对支撑的质量和数量都有影响,支撑易受残留牙嵴减少 (RRR) 的影响
- 支撑义齿的粘膜、粘膜下层和下面牙槽骨支撑在适应能力和义齿移动的耐受性方面存在限制,具体与时间有关
- 义齿松动会影响功能(话说、咀嚼)并造成各种临床反应,如义齿口腔黏膜炎、念珠菌感染、刺激增生、牙槽嵴松软等。
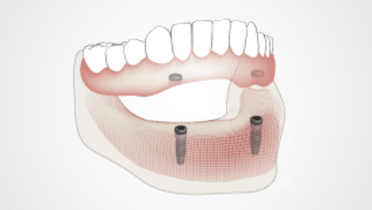
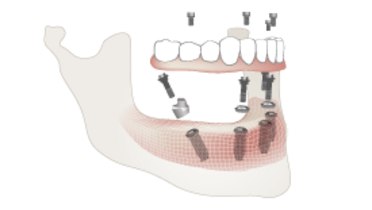
- 如果患者不满足于配戴全口义齿的生活质量,应认真考虑口腔种植体治疗。
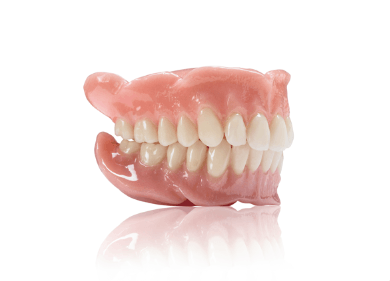
全口义齿治疗
研究和临床实验表明,大部分缺齿人群可接受传统全口义齿。对全口义齿感到满意的配戴者都能很好地适应口腔修复,并学习配戴义齿吃饭和说话。通常认为,配戴义齿的理想预后情况包括牙嵴健康且萎缩程度低,并且咬合设计良好。但是,制作理想的传统全口义齿并不是缺齿者的灵丹妙药;很多患者在修复过程中存在适应不良的问题,难以适应全口义齿,认为生活质量受到影响。
全口义齿 — 功能注意事项
传统全口义齿的基座是下层粘膜、粘膜下层和牙槽骨。所有这些组织的适应能力有限,无法提供牙齿和牙周韧带或骨结合口腔种植体所具有的功能水平。口腔内肌肉的活动,特别是舌头的活动会导致义齿松动,影响患者的说话和咀嚼功能。严重牙嵴萎缩的特征为义齿配戴区域变平。在这些情况下,义齿会在水平方向上自由滑动。如果无法获得令人满意的生活质量,就需要借助口腔种植体固定来固定义齿并保持义齿稳定。如果患者难以配戴全口义齿,种植体覆盖义齿或固定种植体修复体可以显著降低随着时间推移对牙槽骨和功能效率的影响。