-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
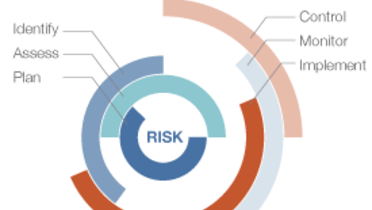
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
局部病史
Key points
- 检查颜面结构有无不对称、先天异常、血管瘤
- 评估口腔状况,特别是现有牙周炎和/或颞下颌关节功能障碍 (TMD) 历史
- 治疗和控制现有牙周炎和 TMD 至关重要
- 由于某些口腔颌症状,可采用非种植体疗法
口腔-颌区域既往病史基本情况
完整既往病史的关键问题包括: 张口度, 唾液分泌量, 是否存在粘膜疾病、牙龈健康状况、之前牙周手术的体征、牙齿运动过大、TMJ 问题、矫正治疗、味觉障碍、口腔异味/口臭、舌苔和口腔卫生。
牙周和牙龈状况、口腔卫生
齿龈炎不一定是影响种植体治疗的因素,但菌斑堆积和口腔卫生不良都会成为影响长期维护粘膜和种植体周边组织水平的重要因素,还能体现出患者以往的卫生态度。
如果手术和/或保守治疗以及充分的口咽卫生都无法成功治疗和控制 现有牙周炎 应考虑选择非种植体治疗。
应评估患者的口腔卫生动机和可能性。如果动机不充分缺乏卫生方案,如患者体弱或患者视力减退、体力减弱,无法进行充分的口腔卫生保持工作,应考虑选择非种植体修复。
手术或外伤史
对以前进行的颌面部手术及其对张口度和骨质骨量的影响、解剖结构标记保留、软组织状况、植入韧带、鼻窦、下颌神经等进行完整评估。特别注意手术和外伤后的骨质缺损和骨高度偏差。如果需要,应考虑使用其他诊断支持方法,如全景 X射线, CBCT等。
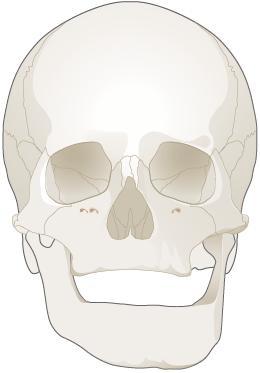
TMD
(TMD).这就需要评估关节炎、外伤、牙咬合不正、叩齿、张口度有限/降低、疼痛、偏头痛的历史或迹象以及其他咬合不良迹象。如果需要,临床医师可考虑使用其他诊断支持方法,如全景 X 射线、CT 或 MRI,以影像方式显示软组织状况(间盘)。在发生创伤性牙合的情况下,可能需要识别和纠正修复并对咬合功能进行设计。为了缓解肌肉系统/痉挛和关节疼痛,并解决难治性 TMD,可转诊至治疗 TMD 的专家。未治疗或无法治疗的 TMD 是种植体治疗的禁忌证。
主题
Related articles
Digital Textbooks
Biomechanical studies of the relationship between and cranial form and function have frequently appeared in dental and engineering literature since the mid-to-late 90s. It is known that deformation of the cranial vault occurs during contraction of the temporalis muscle, most particularly the anterior portion of the muscle Craniofacial osseous stress and strain occurring during mastication is moderated by the unique, complex suture types found throughout the skull.