-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
硬组织处理 - 下颌
Key points
- 拔牙后出现硬组织和相邻软组织萎缩
- 骨量不足需要执行再生程序
- 可以对骨再生程序使用骨或不同的骨替代材料
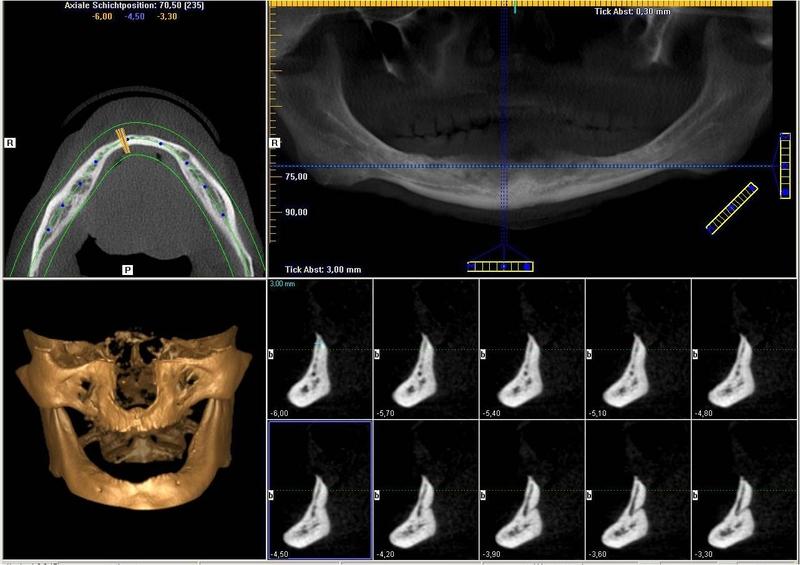
骨高度评估
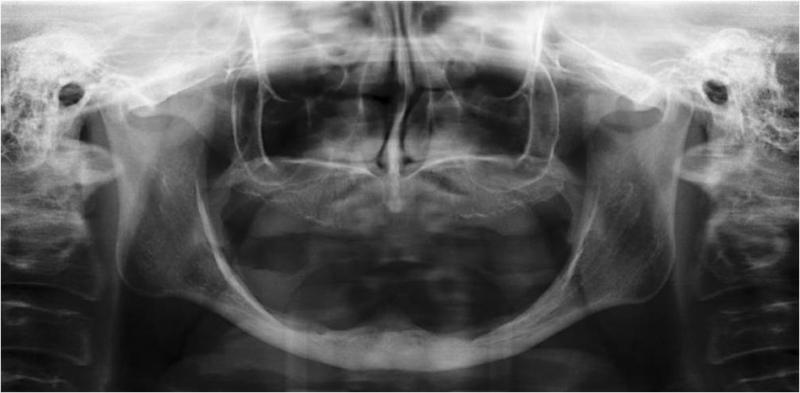
科学文献表明,长度 ≥ 6 mm 的短型种植体能够在缺齿下颌中支撑修复体。拔除牙齿后,下颌显示出不同程度的萎缩(图 1 和 2)。关于硬组织处理,必须确定下颌的哪些区域受影响。下颌的颌孔间区域通常可提供足够的骨高度用以植入牙科种植体(图 3)。不过,如果下颌后部显示下颌神经上方 >6 mm 的骨高度降低,则在植入种植体之前需要进行骨再生。
垂直缺损的治疗选项
- 移植(使用自体骨、冻干骨或骨替代材料)
- 截骨术(骨或骨替代材料介入)
- 牵拉成骨技术。执行截骨术后,临时插入牵拉设备,并将两部分分开,直到达到所需的牵拉高度
- 下颌神经的偏侧性
水平缺损的治疗选项
- 移植(使用自体骨或骨替代材料)
- 牙嵴骨劈开术(在种植体植入之前,用骨凿增加水平宽度,然后使用骨凿或骨扩张器)
- 骨的校平(如果水平维度允许执行此程序)
为了最全面地保护下颌神经,种植前成像(3D 成像工具)可帮助清楚地标识下颌管的位置(图 4)。