-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
CBCT
Key points
- CBCTはスパイラルCTと比較して照射線量が少なくなります。
- 照射線量はmAおよび被曝時間に依存し、ボクセルサイズには依存しません。
- 寸法精度は高いことが証明されています。
- 種々のハードウェアにより、臨床適応に応じたさまざまなFOVが得られます(4×4~15×20cm等)。
- 2次元画像と3次元画像の両方を獲得することができます。
- スパイラルCTのハンスフィールド値ほどの信頼性は高くはありません。
- 治療計画において使用予定または使用中の補綴装置を画像に組み込むことができるのは、非常に有益です。
CBCTに関する注意事項
- 線源でコリメートされたX線が扇型に照射され、検出器に到達します。これがコーンビームです。
- ピクセル(picture+element)は2次元画像の最小要素であり、ボクセルは3次元画像の最小要素です。
- 大FOVは、両顎とその関係を視覚化します。
- 小FOVは、骨梁および皮質骨の詳細な画像を提供します。
- グレースケール値は組織によって異なり、その信頼性はスパイラルCTほど高くはありません。
- CBCTは、切歯管、舌側の骨陥没および皮質骨の欠損といったパノラマ/口内法X線撮影では確認できない臨床的に重要な構造を検出することができます。
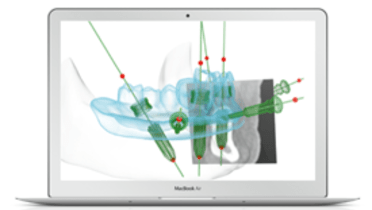
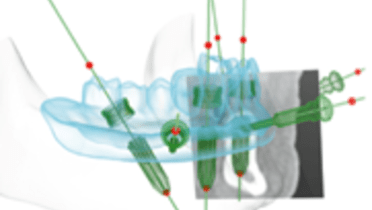
- 切歯管の近心部をとらえたCBCTの 2次元画像です。
- 術前計画やドリルガイドまたは補綴物のCAD-CAM製作にはCBCTが不可欠です。
- グレー値を除けば、CBCTはスパイラルCTと比較して同等もしくはそれ以上の優れた情報を提供し、放射線被曝量やコストも低くなります。
臨床トピック
Related articles
Additional external resources
Questions
ログインまたはご登録してコメントを投稿してください。
質問する
ログインまたは、無料でご登録して続行してください
You have reached the limit of content accessible without log in or this content requires log in. Log in or sign up now to get unlimited access to all FOR online resources.
FORウェブサイトにご登録していただきますと、すべてのオンライン・リソースに無制限にアクセスできます。FORウェブサイトへのご登録は無料となっております。