-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
アバットメントの材料
Key points
- アバットメントはインプラントと修復物との間に介在する部品であり、通常、インプラントにスクリューで固定されます。
- アバットメントは、保定力、支持、安定性および最終的な修復に必要となる最適な位置を提供します。
- チタンおよびジルコニアがアバットメントの製作に最も一般的に使用される材料です。
- アバットメントはメーカーによって製作されるか、CAD/CAMにより患者に合わせて製作されます。
アバットメントの種類と選択-概論
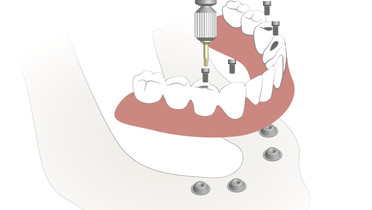
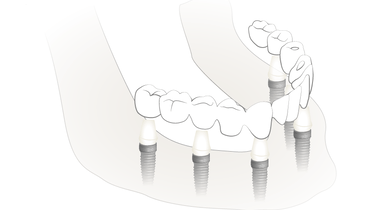
インプラントベースの補綴物はセメント固定、スクリュー固定、またはその両方の組み合わせによって固定されます(図1)。当然のことながら、アバットメントは、インプラントと修復物との間に介在する部品であり、通常、インプラントにスクリューで固定されます。アバットメントは、保定力、支持、安定性および最終的な修復に必要となる最適な位置を提供します。その他利用可能な選択肢 (ロッキングテーパー、アバットメントがインプラントの一部になっている1ピースインプラント) がありますが、コンセプトが補綴物の選択に対してあまり柔軟性がないため、あまり一般的ではありません。
アバットメントの材料
アバットメントは、一般的に、歯科技工所で患者に合わせて設計/製作されるか、インプラントメーカーによって製作されます。
最も一般的なアバットメントの材料は以下の通りです。
- チタン
- ジルコニア
- 鋳造用貴合金(UCLAアバットメント、伸縮自在のクラウン)
- 樹脂
- PEEK(ピーク)(ポリエーテルケトン)
インプラント・アバットメントは、通常、文章で十分に裏付けられた生体適合性および力学的性質により、外科用チタン合金で製作されますが、チタン製アバットメントは生体力学的な観点から大変安定しているにもかかわらず、見た目に関わる部分に使用する場合には限界があります。前方部では、機能中に目に見えると、色と形の観点から、補綴物-インプラントの合成物と歯肉間の調和が重要な役割を持ち、その点、チタン製アバットメントに代わる材料としてジルコニアが推奨されます。ジルコニア製アバットメントは完全にジルコニアだけで、または-形、メーカーおよび強度に応じて-中核部をチタンで製作して利用することができます。金属核に代わるものとしては、チェアサイドで患者に合った設計をし、ジルコニア製アバットメントを製作し、金属のアダプターに接着させるものがあります。
個別にワックスされ、鋳造されるUCLAタイプのアバットメントは人気を失い、CAD/CAM によって製作または既製されたものに入れ替わりましたが、鋳造技術は伸縮自在のクラウンによって固定されるオーバーデンチャーの設計および製作するための選択肢の一つです。
樹脂およびPEEK(ピーク)タイプのアバットメントは、通常、一時的に使用する場合および暫定的に修復する場合にのみ望ましいものです。

is there any evidence where they have compared all materials used to make abutments and compared their success rates ?
is there any evidence where they have compared all materials used to make abutments and compared their success rates ?
is there any evidence where they have compared all materials used to make abutments and compared their success rates ?