-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
硬組織の管理-下顎
Key points
- 抜歯後、硬組織および周囲の軟組織が萎縮します。
- 骨量が不十分の場合は、増生手術が必要です。
- 骨または各種の代用骨材料を増生手術に利用することが可能です。
骨の高さ評価
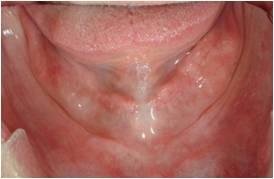
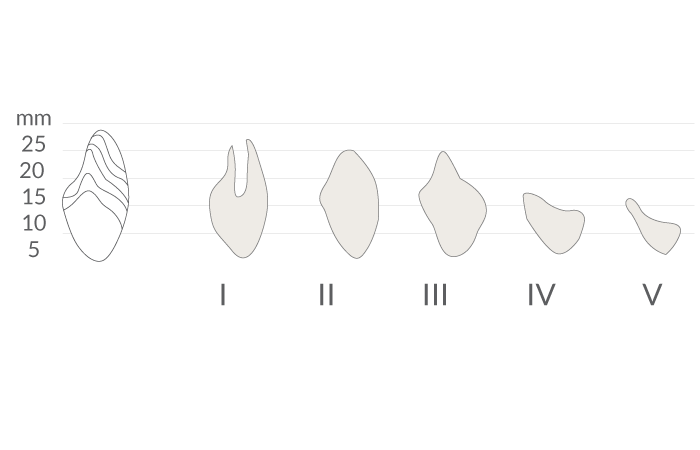
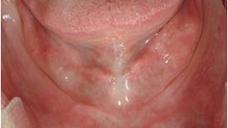
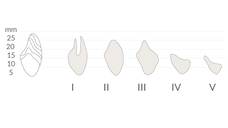
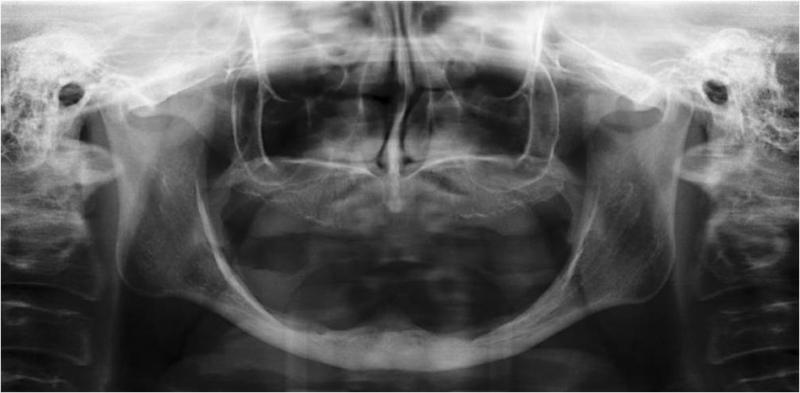
文献により、下顎では長さ≧6mmの短いインプラントで補綴物を支持できることが示されています。抜歯後、下顎は様々な度合いの萎縮を示します(図1、2)。硬組織の治療に関しては、下顎のいずれの部位が影響を受けているか判断する必要があります。多くの場合、下顎のオトガイ間領域(interforaminal region)はインプラント埋入に適切な骨の高さがあります(図3)。しかし、下顎臼歯部が下顎神経の上で骨の高さが6mm以下の場合は、インプラント埋入前に骨増生が必要となります。
垂直的吸収の場合の治療選択肢
- 移植(自家骨、凍結乾燥骨または代用骨材料を使用)
- 骨切り術(骨の中間挿入物または代用骨材料を使用)
- 仮骨延長。骨切り術後、伸延器具を一時的に挿入し、望ましい伸延の高さを得るまで2つのセグメントを分離
- 下顎神経の側方移動術
水平的呼吸の場合の治療選択肢
- 移植(自家骨または代用骨材料を使用)
- 顎堤分割(インプラント埋入に先立ち、のみを用いて、続いてオステオトームまたは骨エキスパンダーにより水平幅を拡大)
- 骨のレベリング(水平寸法がこの手術を許容する場合)
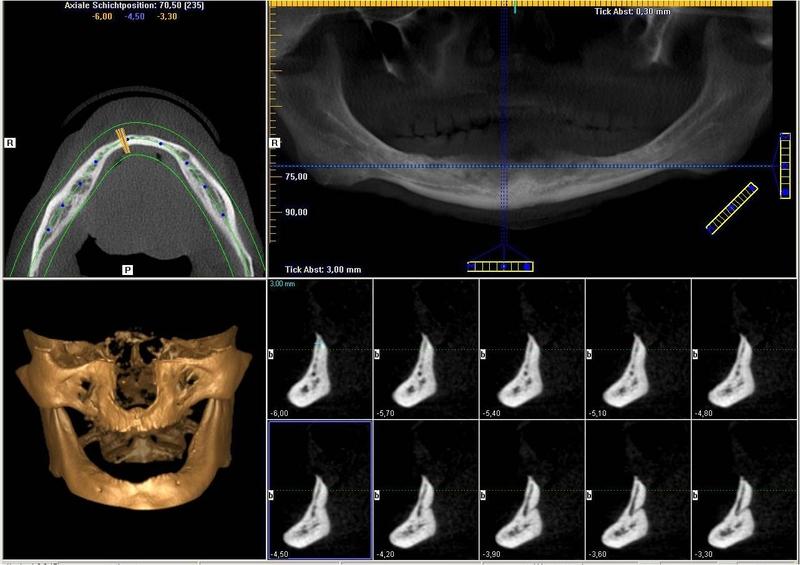
下顎神経を最大限保護するため、インプラント前の画像診断(3D画像化ツール)は、下顎管の位置を明確に特定するのに有用です(図4)。
臨床トピック
Questions
ログインまたはご登録してコメントを投稿してください。
質問する
ログインまたは、無料でご登録して続行してください
You have reached the limit of content accessible without log in or this content requires log in. Log in or sign up now to get unlimited access to all FOR online resources.
FORウェブサイトにご登録していただきますと、すべてのオンライン・リソースに無制限にアクセスできます。FORウェブサイトへのご登録は無料となっております。