-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
歯槽頂/傍歯槽頂切開
Key points
- 全層弁を確保するため、切開時はブレードを骨に接触させなくてはなりません。
- インプラント/アバットメント周囲の非可動性組織に配慮して角化組織を分離しなくてはなりません。
切開 - 一般的注意事項
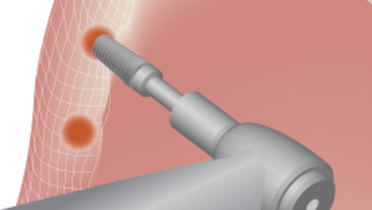
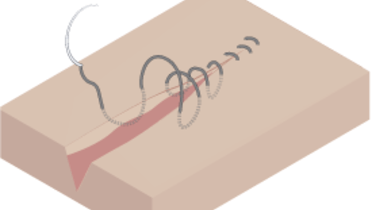
いずれの口腔内手術も切開で始まり、縫合または接着で終わります。歯槽頂切開の適応は、インプラントまたはアバットメントがノンサブマージ型で、埋入後も粘膜を貫通して口腔内に露出する1回法の手術です。一般的な手術原則として、サブマージしている異物の上に切開を入れることは推奨されません。しかし、歯槽頂切開と傍歯槽頂切開の比較試験では、骨内インプラントの転帰には差がないことが明らかになりました。
フラップへの血液供給を確保するため、組織は丁寧に扱い、手術部位の視認性を確保するため、骨を覆う血液はできるだけ少なくします。
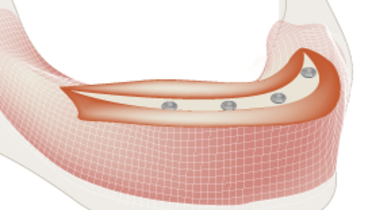
上顎
上顎では、歯槽頂より口蓋側に(palatal-crestally)切開を入れます。術野の視認性を確保するため、フラップは全層とします。通常、フラップには柔軟性がないため、遠心部に縦切開を入れる必要があります。フラップ挙上後、鼻孔底、鼻口蓋管、頬側壁および口蓋側壁の視認性を確保する必要があります。
頬骨インプラントの場合は、頬骨弓の端および眼窩下孔が見えるように、縦切開を頬骨に向かってさらに長く延長しなくてはなりません。
<span itemprop="name" content="crestal incision_max_malo"></span> <span itemprop="description" content=""></span> <span itemprop="duration" content="186"></span> <span itemprop="thumbnail" content="http://cdnbakmi.kaltura.com/p/1320171/sp/132017100/thumbnail/entry_id/1_gxvlnalx/version/100000/acv/181"></span> <span itemprop="width" content="560"></span> <span itemprop="height" content="395"></span>
下顎
下顎無歯顎では、概ね角化歯肉が退縮しています。切開時は、オトガイ孔の位置を考慮に入れます。オトガイ孔が歯槽頂の上端に位置するような重度吸収下顎骨を取り扱う際は、フラップの完全な可動性を得るため、正中線に縦切開を入れることもできます。フラップ挙上後、オトガイ孔、頬側壁および舌側壁の視覚化を含め、完璧な術野を確保する必要があります。