-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
2回法または1回法
Key points
- オッセオインテグレーションは、インプラントの長期的な臨床的成功の前提条件です。
- オッセオインテグレーションにとって決定的に重要な要素は、インプラント周囲の炎症と動きが最小限であることです。
- 完全被覆のインプラントの場合は、2回目の外科的アプローチが必要となります。
インプラント埋入方法
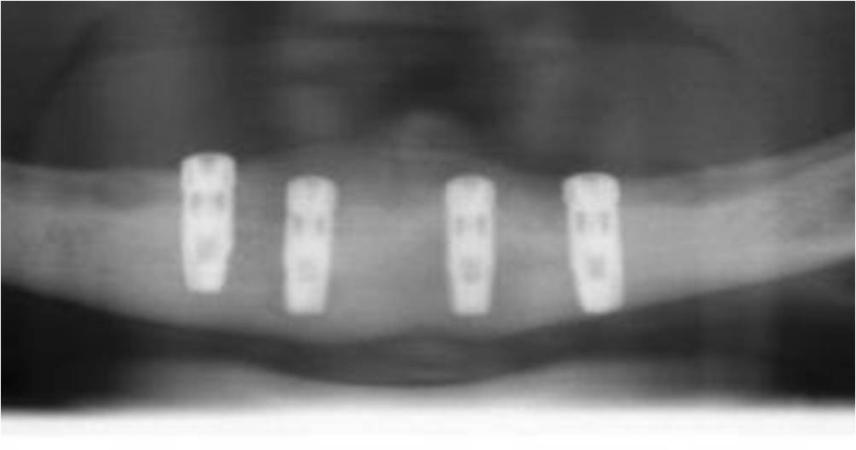
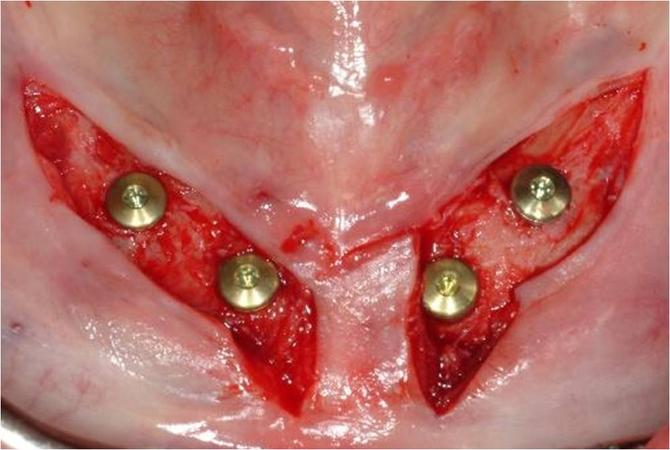
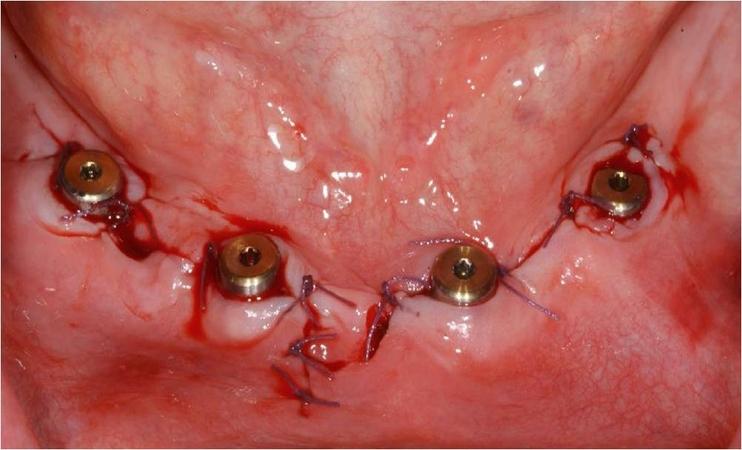
インプラント埋入方法には、2回法インプラント埋入と1回法インプラント埋入の2種類あります(図1)。

インプラントと顎骨の結合および外科手術の原則
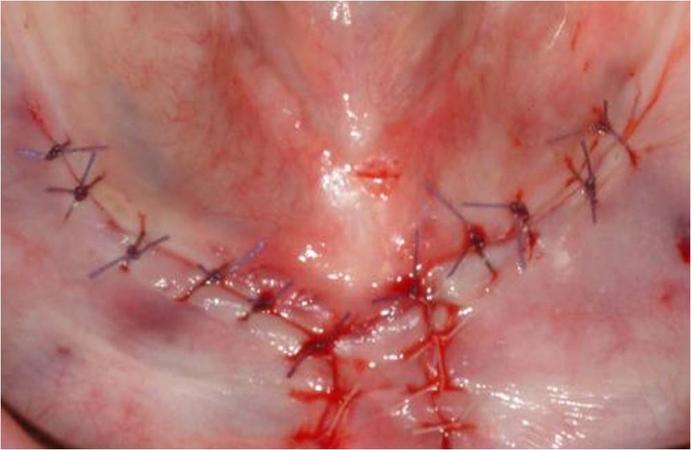
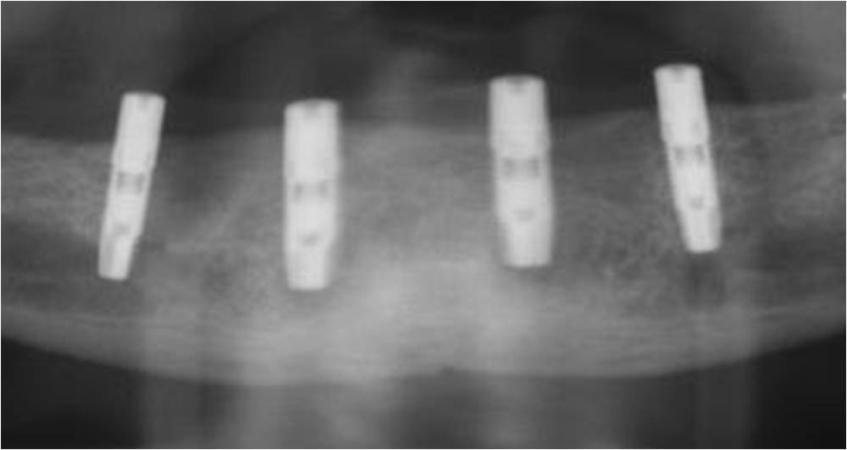
口腔骨内インプラントは、無歯顎においても長期的に成功しています。インプラントは、埋入後に骨結合します。このプロセスは、骨とインプラント表面の密接な接触を築くものです。骨のインプラントへの直接結合は、インプラントの成功を導きます。インプラント周囲組織の炎症および/またはインプラントの動きは、骨結合プロセスを損ないます。骨結合低下のリスクを最小限にするため、下顎では、インプラントを骨内に埋入(二回法インプラント)し、その状態で3カ月間の治癒期間を設けることが歴史的に推奨されてきました(図1、2)。3カ月後、二次手術でインプラントを露出させます(図2 a~c)。
その後の臨床研究により、1回法インプラントが2回法インプラントと同等の長期的成功を挙げたことが示されています。
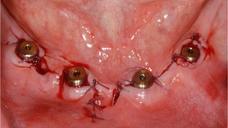
1回法インプラント埋入の治療概念は、患者に対し早期のインプラント負荷および治療期間の短縮を可能にします(図3 a~b、表1)。
2回法インプラント埋入は、骨質が悪く埋入時に十分な初期固定が得られない状態や、炎症リスクが高い状態(放射線照射顎骨または骨増生手術後など)において依然として推奨されています(表1)。
|
2回法インプラント |
1回法インプラント |
インプラントの骨結合 |
>95 % |
|
治療期間の長さ |
2~3カ月 |
即時荷重、早期荷重のプロトコルが可能 |
適応 |
インプラントの初期固定不良、骨および粘膜の損傷 |
インプラントの十分な初期固定、炎症リスクがないこと |
|
二次手術の必要性
|
インプラントの露出手術が必要 |
これ以上の手術は不要 |