-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
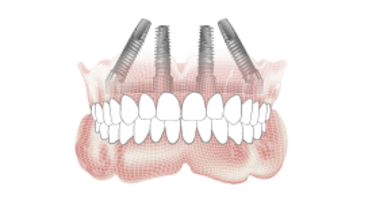
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
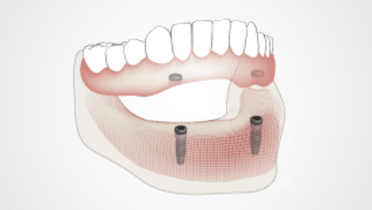
Overdenture Clinical Protocol
Key points
- The oral rehabilitation of edentulous patients is comprised of specific clinical techniques
- Clinical objectives are best met by following a routine protocol
- Restoration of soft tissue health is an important prerequisite for impression making
Overdenture clinical protocols
Successful oral rehabilitation of edentulous patients with removable prostheses demands careful adherence to a clinical protocol.
Clinical objectives are met by using a routine clinical protocol that includes most or all of the following steps:
-
Restoration of soft tissue health. Absence of a wide band of attached mucosa does not seem to adversely affect soft tissue health around implants. Gingival-mucosal grafting procedures are rarely prescribed. Irreversible hydrocolloid impressions in stock trays are made to produce required stone diagnostic casts.
-
Fabrication of custom impression trays and making of final impressions using elastomeric materials in conjunction with recording functional border extensions of the prosthesis. Definitive stone casts are then poured.
-
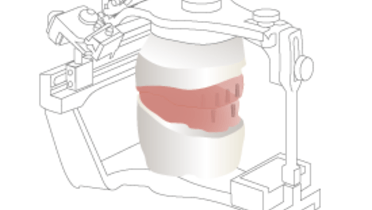
Fabrication and adjustment of wax occlusion rims to establish height of the occlusal plane, while establishing correct vertical dimension of occlusion, suitable smile and lip lines.
-
Registration of the maxillo-mandibular relation record and articulator mounting (with or without use of a face-bow).
-
Artificial teeth selection and their arrangement for a try-in of the provisional set-up
-
Clinical evaluation of the desired restoration of vertical and horizontal jaw dimensions, centric relation and overall esthetic outcomes.
-
Denture placement to include evaluation of patient comfort, function and esthetic appearance. Overdenture is related to attachments. Careful attention must be paid to denture base fit and extensions, functional elements of speech and mastication, occlusion, and appearance/soft tissue support.
-
Post-placement evaluation of patient comfort, function and esthetics. Adjustments are made as necessary.