-
0
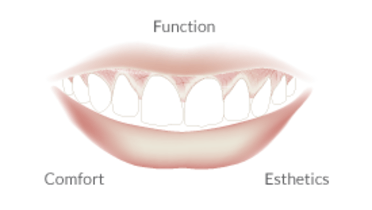
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
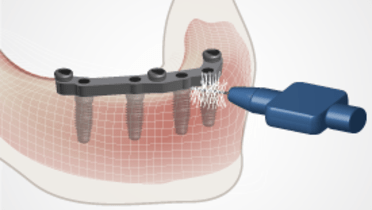
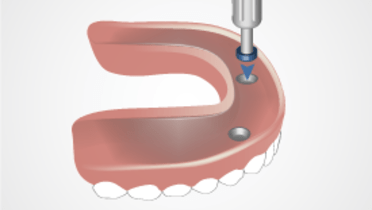
Implant Overdenture post-placement
Key points
- Evaluation of overdenture base fit, extension, occlusion and function, esthetics and comfort
- Healing of soft and hard tissue should be evaluated
- Resilient relining material should be replaced if necessary
- Check of prosthetic component function and proper handling of the overdenture by the patient
Post-placement visits - considerations
At post-placement visits, the same factors evaluated carefully at the placement appointment should be reviewed and adjusted where necessary. Overdenture base fit, extensions, occlusion, esthetics, function, comfort and overall patient satisfaction need to be checked. Also, the clinician should assess soft tissue healing and any residual swelling. If a resilient liner was placed, healing and shrinkage of soft tissues may result in poor denture base fit necessitating replacement of the liner. For most resilient liners, the mechanical properties are such that replacement every 2-4 weeks is indicated. Over the long-term, when denture base fit worsens with ongoing resorptive and morphological changes, a definitive reline of the denture base is indicated. In addition, loss of retention may require modification of attachments or replacement of either the matrix or patrix elements depending upon the specific retention mechanism chosen.
Patient response
Post-placement visits are of great importance for assessing the patient's response to the esthetic outcome along with reviewing the patient's adaptability to the new prostheses and general satisfacation with the restoration. Some patients choose a removable option initially only to find that they wish to switch to a fixed prosthesis once they experience daily living with a removable prosthesis. In these instances, additional implants and prosthetic re-design are likely indicated. Regardless of whether the patient likes or dislikes the overdenture, the prosthesis has served a valuable purpose in directing additional implant care to increase the probability of a satisfied patient.