-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
Implant overdenture trial placement
Key points
- The trial insertion appointment is a significant step for first evaluation of and decision on the prosthetic design and is critical for successful edentulous patient care
- Sufficient interocclusal space for overdenture components is necessary
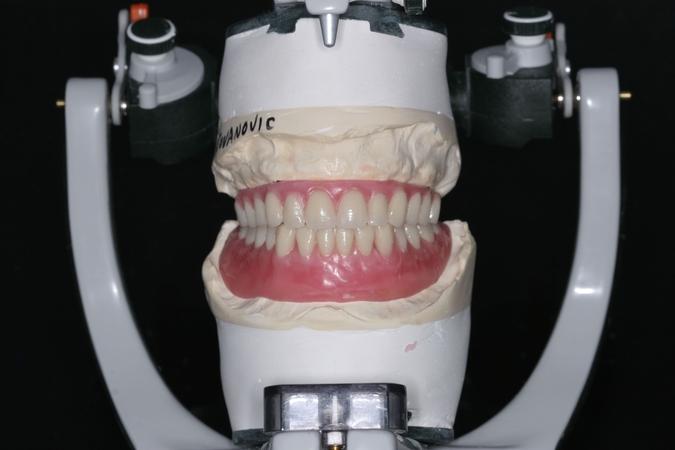
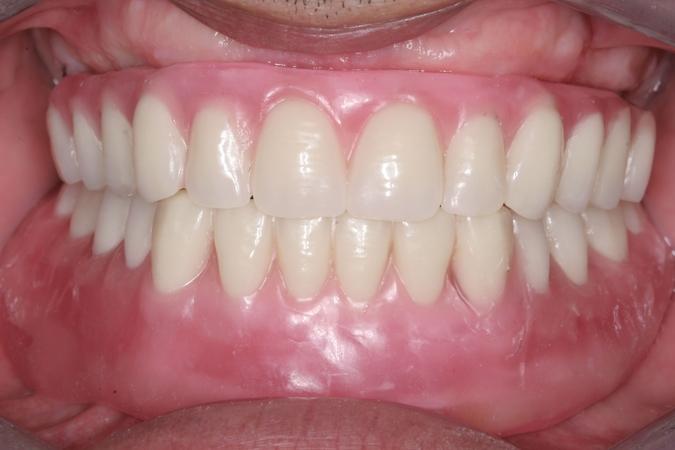
Trial placement - functional and esthetic evaluation
The trial placement appointment is a significant one for successful edentulous patient care.
The tooth arrangement (set-up) provides a tangible orientation index of the teeth’s spatial positions in relation to each edentulous arch. This clinical visualization addresses both dentist and patient mediated esthetic and technical considerations. It employs the laboratory prepared provisional teeth setup on an articulator, thereby simulating jaw and teeth contact movement relationships and movement.
The trial placement appointment represents the first time that dentist and patient can see what has been created in the laboratory; and a decision will then be one of acceptance, modification or change. This is the first occasion where the patient can see what the dentures will look like and the patient should be actively engaged and offered the chance to request changes. Mutual satisfaction with the provisional waxed-up result should be reached before additional clinical steps are taken e.g. processing the dentures. A patient who has reservations and is not able to express them will likely be dissatisfied with the finished dentures. It is important to not just focus on the tooth arrangement, but also pay close attention to the contour of the wax-up. If the wax-up is too bulky, it is better to remove the bulk before processing and if the wax-up is insufficient, then wax should be added before processing. Once it is approved of, the trial arrangement and wax-up is accordingly processed.
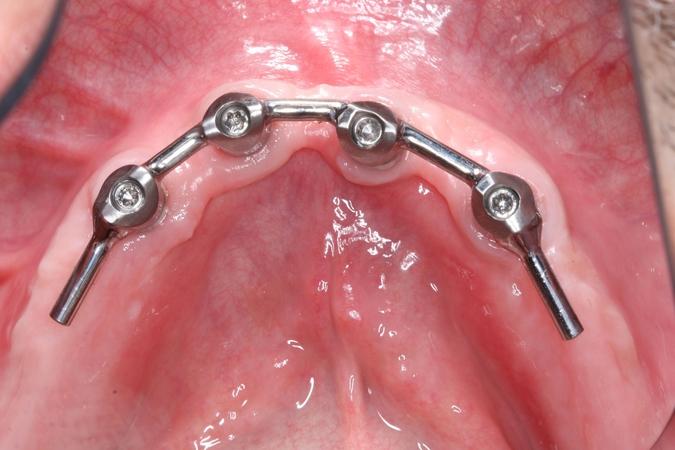
Overdenture and interocclusal space considerations
The trial placement offers the chance to evaluate whether tooth position needs to be modified relative to the interocclusal space needed for overdenture abutments and attachments. If insufficient interocclusal space is present, a modification of the treatment plan may be necessary either by eliminating the bar when a bar had been planned or else using shorter profile abutments. If modifications are not made, the final prosthesis will be either too thin in some areas and prone to fracture or will need to be too bulky for patient comfort and function.
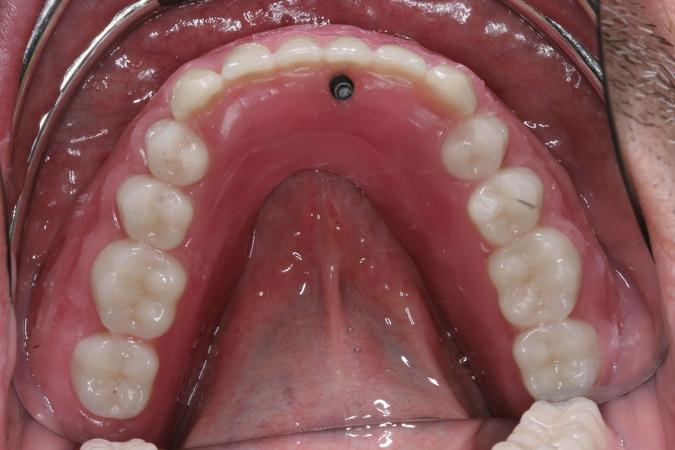
In situations of immediate loading, consideration is also given to the type of planned surgical approach and implant system selection. This is because trans-mucosal healing abutments may be used to provide stability if the prosthesis is relined with a resilient lining material on the day of surgery.

Is this a free clinical trial
Is this a free clinical trial?
Is this a free clinical trial?