-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient Demand
- 0.2 Anatomical location
-
0.3
Patient History
- 2.1 General patient history
- 2.2 Local history
-
0.4
Risk Assessment
- 3.1 Risk Assessment Overview
- 3.2 Age
- 3.3 Patient Compliance
- 3.4 Smoking
- 3.5 Drug Abuse
- 3.6 Recreational Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- 3.7 Condition of Natural Teeth
- 3.8 Parafunctions
- 3.9 Diabetes
- 3.10 Anticoagulants
- 3.11 Osteoporosis
- 3.12 Bisphosphonates
- 3.13 MRONJ
- 3.14 Steroids
- 3.15 Radiotherapy
- 3.16 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
2
Treatment Options
-
2.1
Treatment planning
- 0.1 Non-implant based treatment options
- 0.2 Treatment planning conventional, model based, non-guided, semi-guided
- 0.3 Digital treatment planning
- 0.4 NobelClinician and digital workflow
- 0.5 Implant position considerations overview
- 0.6 Soft tissue condition and morphology
- 0.7 Site development, soft tissue management
- 0.8 Hard tissue and bone quality
- 0.9 Site development, hard tissue management
- 0.10 Time to function
- 0.11 Submerged vs non-submerged
- 0.12 Healed or fresh extraction socket
- 0.13 Screw-retained vs. cement-retained
- 0.14 Angulated Screw Channel system (ASC)
- 2.2 Treatment options esthetic zone
- 2.3 Treatment options posterior zone
- 2.4 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
2.1
Treatment planning
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
- 0.1 Anesthesia
- 0.2 peri-operative care
- 0.3 Flap- or flapless
- 0.4 Non-guided protocol
- 0.5 Semi-guided protocol
- 0.6 Guided protocol overview
- 0.7 Guided protocol NobelGuide
- 0.8 Parallel implant placement considerations
- 0.9 Tapered implant placement considerations
- 0.10 3D implant position
- 0.11 Implant insertion torque
- 0.12 Intra-operative complications
- 0.13 Impression procedures, digital impressions, intraoral scanning
- 3.2 Treatment procedures esthetic zone surgical
- 3.3 Treatment procedures esthetic zone prosthetic
- 3.4 Treatment procedures posterior zone surgical
- 3.5 Treatment procedures posterior zone prosthetic
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
-
4
Aftercare
Site development, hard tissue management
Key points
- Reduced bone volume or unfavorable shape of alveolar bone may require bone augmentation prior to implant placement.
- Depending on shape of bone defect horizontal or vertical graft procedures are applied.
- For a better diagnosis 3-D computed tomography is preferred.
- With limited bone volume for implant placement, always consider treatment alternatives, such as a short implant, a tooth-supported 3-unit bridge, orthodontics, or no treatment at all.
Bone height and width evaluation
3-D imaging seems the best option unless clinical examination reveals an ample bone volume. The local bone texture may be clearly visible if cross-sectional images are available or it may be approximated from the trabecular pattern of 2-D images. Panoramic radiographs reveal the morphology of the sinuses and may give a hint of available bone height above the lower alveolar nerve.
Anterior maxilla:
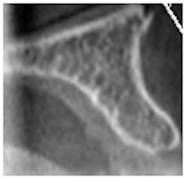
Figure 1: Excessive bone volume
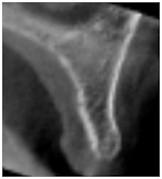
Figure 2: Sufficient bone volume
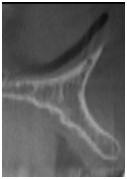
Figure 3: Insufficient bone volume
Obtained cross-sectional images of anterior maxillae presenting with various horizontal bone dimensions
Posterior mandible:
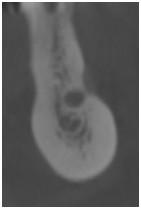
Figure 4: Excessive bone volume
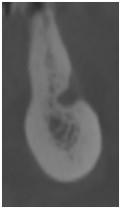
Figure 5: Sufficient bone volume
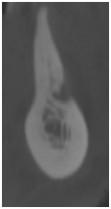
Figure 6: Insufficient bone volume
Obtained cross-sectional images of posterior mandibles presenting with various horizontal bone dimensions in regions of the lower alveolar nerve and mental foramen
Treatment options for vertical and horizontal deficiency
If the available bone volume does not allow for implant placement, buccal/crestal onlay grafts (autografts, allografts, xenografts, and alloplasts, alone or in combination) have proven to offer a reliable outcome. Those can be fixed or stabilized by means of mini-screws and covered with collagen membranes. Anorganic bovine bone substitutes (xenografts) are comparable to particulated autografts in terms of implant survival and newly formed bone. Importantly Anorganic Bovine Bone is considered to be a non-resorbable bone substitute, forming a composite with newly formed bone and therefore may reduce bone resorption processes over time and guarantee long-term implant stability.
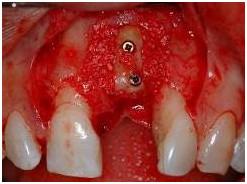
Figure 7: Buccal onlay autograft in upper left central incisor region fixed with 2 mini-screws. Additional xenogenic bone particles before covering with collagen membrane.
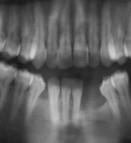
Figure 8

Figure 9
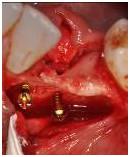
Figure 10
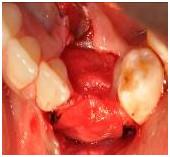
Figure 11
Aplasia of lower canines and missing lower left lateral incisor. Insufficient bucco-lingual bone dimension (cross-sectional image). Two mini-screws to stabilize xenogenic bone particles and a covering collagen membrane
Cutting off the incisal nerve, together with bone fill of the incisive canal, does not seem to cause major symptoms and can provide a solution in some patients with very limited bone volume in upper central incisor position.
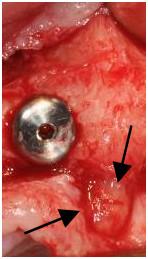
Figure 12: Implant in upper right central incisor position in close relation to a prominent incisal foramen and nerve (arrows)
In the dorsal areas sinus inlay procedures or elevation of the mucosal lining offer reliable outcomes. Sinus floor augmentation can be performed as a one- or two-stage approach with simultaneous or delayed implant placement depending on the primary implant stability. With a residual alveolar bone height of ≥3-4 mm implants are inserted simultaneously with sinus grafting. A two-step procedure is recommended in cases of less than 4 mm where sufficient primary implant stability is not likely to be achieved. A delayed implant insertion is then performed after 4-6 months of healing.
Loading of the implants inserted in the augmented sinus is recommended after 4-6 months.
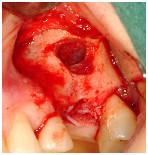
Figure 13
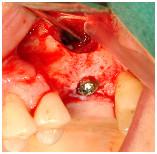
Figure 14
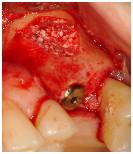
Figure 15
Lateral sinus floor elevation in left first molar region with simultaneous implant placement and xenogenic bone particles around the implant apex
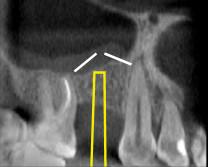
Figure 16: Schematic illustration of sinus floor elevation via the crestal approach in right first molar region. Osteotome (yellow) hammered to cause an upward greenstick sinus floor fracture (white)
With limited bone volume above the mental foramen or lower alveolar nerve always consider to replace a missing tooth with a short implant, with a conventional tooth-supported bridge, or no treatment at all.
Figure 17
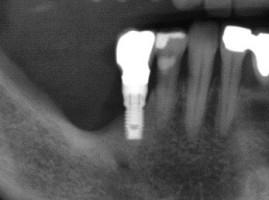
Figure 18
Close relation between mandibular crest and right mental foramen. A short implant replacing the right second bicuspid