-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient Demand
- 0.2 Anatomical location
-
0.3
Patient History
- 2.1 General patient history
- 2.2 Local history
-
0.4
Risk Assessment
- 3.1 Risk Assessment Overview
- 3.2 Age
- 3.3 Patient Compliance
- 3.4 Smoking
- 3.5 Drug Abuse
- 3.6 Recreational Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- 3.7 Condition of Natural Teeth
- 3.8 Parafunctions
- 3.9 Diabetes
- 3.10 Anticoagulants
- 3.11 Osteoporosis
- 3.12 Bisphosphonates
- 3.13 MRONJ
- 3.14 Steroids
- 3.15 Radiotherapy
- 3.16 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
2
Treatment Options
-
2.1
Treatment planning
- 0.1 Non-implant based treatment options
- 0.2 Treatment planning conventional, model based, non-guided, semi-guided
- 0.3 Digital treatment planning
- 0.4 NobelClinician and digital workflow
- 0.5 Implant position considerations overview
- 0.6 Soft tissue condition and morphology
- 0.7 Site development, soft tissue management
- 0.8 Hard tissue and bone quality
- 0.9 Site development, hard tissue management
- 0.10 Time to function
- 0.11 Submerged vs non-submerged
- 0.12 Healed or fresh extraction socket
- 0.13 Screw-retained vs. cement-retained
- 0.14 Angulated Screw Channel system (ASC)
- 2.2 Treatment options esthetic zone
- 2.3 Treatment options posterior zone
- 2.4 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
2.1
Treatment planning
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
- 0.1 Anesthesia
- 0.2 peri-operative care
- 0.3 Flap- or flapless
- 0.4 Non-guided protocol
- 0.5 Semi-guided protocol
- 0.6 Guided protocol overview
- 0.7 Guided protocol NobelGuide
- 0.8 Parallel implant placement considerations
- 0.9 Tapered implant placement considerations
- 0.10 3D implant position
- 0.11 Implant insertion torque
- 0.12 Intra-operative complications
- 0.13 Impression procedures, digital impressions, intraoral scanning
- 3.2 Treatment procedures esthetic zone surgical
- 3.3 Treatment procedures esthetic zone prosthetic
- 3.4 Treatment procedures posterior zone surgical
- 3.5 Treatment procedures posterior zone prosthetic
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
-
4
Aftercare
サイトデベロップメント、硬組織マネジメント
Key points
- 骨量が少ない場合や歯槽骨の形態が不適切な場合は、インプラント埋入前に骨造成術を行う必要があります。
- 骨欠損の形態に応じて、水平的または垂直的移植術を行います。
- より正確に診断するため、3次元CTの施行が推奨されます。
- インプラント埋入に利用できる骨量が少ない場合は、ショートインプラント、歯牙支持型3ユニットブリッジ、矯正等の代替治療または無治療を検討します。
骨の高さと幅の評価
診査で十分な骨量が認められない場合は、3D撮像が最良の選択であると思われます。断層画像を獲得した場合、または2D画像の骨梁パターンから予測できる場合は、局所骨のテクスチャをはっきりと確認することができます。パノラマX線写真は洞の形状を明らかにし、下歯槽神経の上部の利用可能な骨の高さを確認するための手がかりとなります。
上顎前歯部:
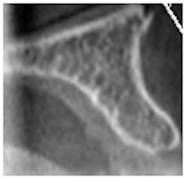
図1:余剰な骨量
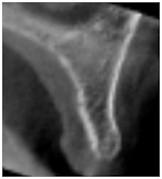
図2:十分な骨量
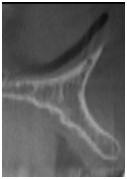
図3:不十分な骨量
さまざまな水平的骨寸法を示す上顎前歯部の断面像
下顎臼歯部:
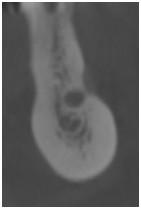
図4:余剰な骨量
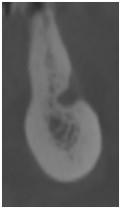
図5:十分な骨量
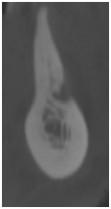
図6:不十分な骨量
下歯槽神経およびオトガイ孔の領域においてさまざまな水平的骨寸法を示す下顎臼歯部の断面像
垂直的および水平的不足に対する治療法の選択肢
インプラント埋入に利用できる骨量が不足している場合は、頬側/頂部へのアンレー移植(自家骨、同種骨、異種骨または人工材料の単独または併用)によって確実な転帰が得られることが実証されています。移植骨はミニスクリューで固定し、コラーゲンメンブレンで被覆することもできます。無機ウシ骨(異種骨)は、粒状自家骨と同等のインプラント残存率および新生骨形成が報告されています。無機ウシ骨は非吸収性の代用骨であり、新生骨とともに複合体を形成するため、経時的な骨吸収を低減し、長期間にわたるインプラントの安定を保証します。
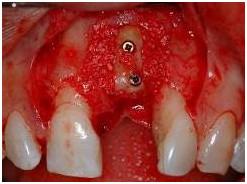
図7:2本のミニスクリューで固定された上顎左側中切歯部の頬側アンレー自家骨移植片。さらに粒状異種骨を移植し、コラーゲンメンブレンで被覆します。
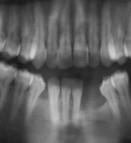
図8

図 9
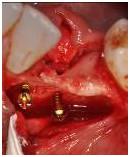
図 10
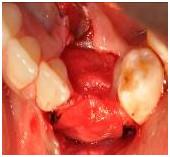
図 11
切歯神経を切断し、切歯管に骨を充填しても、重大な症状は現れないため、上顎中切歯部の骨量がきわめて少ない症例では、解決策の1つとなる可能性があります。
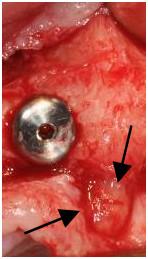
図 12:切歯孔および切歯神経(矢印)と密接な関係にある上顎右側中切歯部のインプラント
臼歯部に関しては、サイナスインレー手術または上顎粘膜の挙上術によって確実な転帰を得ることができます。上顎洞底の造成術を行い、インプラントの初期固定に応じて1回法または2回法として同時または遅延インプラント埋入を行うこともできます。残存歯槽骨の高径が3~4mm以上の場合は、上顎洞の骨移植術と同時にインプラントを埋入します。残存歯槽骨の高径が4mm未満で十分な初期固定が得られそうにない場合は、2回法が推奨されます。この場合は、4~6ヵ月間の治癒期間を置いたのち、遅延インプラント埋入を行います。
骨造成した上顎洞に埋入されたインプラントの負荷は、4~6ヵ月後が推奨されます。
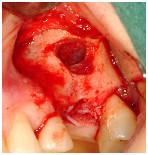
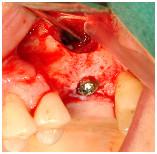
図 14
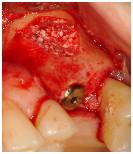
図 15
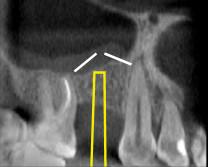
図 16: 右側第1小臼歯部の歯槽頂アプローチによる上顎洞底挙上術。オステオトーム(黄色)で叩き、上顎洞底を上方に向かって若木骨折させます(白色)。
オトガイ孔または下歯槽神経の上部の骨量が少ない場合は、ショートインプラントまたは従来の歯牙支持型ブリッジによる修復、あるいは無治療を検討します。
図 17
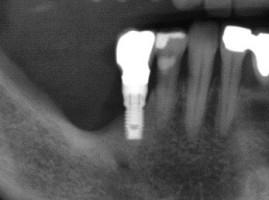
図 18