-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
年龄
Key points
- 针对中年以上患者,应考虑骨代谢减慢以及愈合与整合时间延长的因素。应采用微创手术
- 在直接设计中,针对中年以上患者应考虑修复上部结构,以便轻松采取卫生措施。针对缺齿多年的情况,首选活动修复体
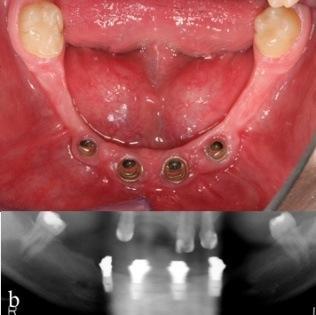
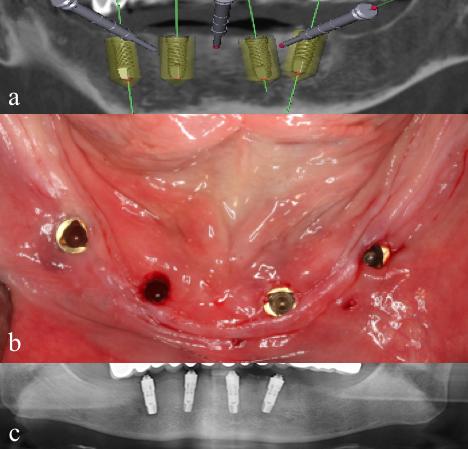
- 对于极少数先天性无牙或缺齿的青少年患者,可在早期考虑种植体支撑的固定替换牙
青少年牙齿发育不全与缺齿
因儿童、青少年乳牙和/或恒齿完全(部分)发育不全导致缺齿的情况非常罕见。通常由外胚层发育不良等潜在疾病导致。这种疾病分为不同类,例如少汗性外胚层发育不良,通常与智力发育障碍有关。青少年缺齿下颌的外观与形状取决于乳牙的情况。
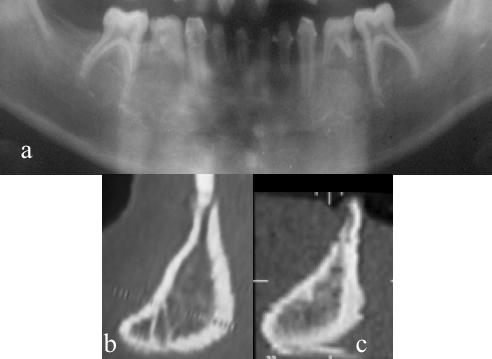
对于乳牙正在发育,但缺失恒牙胚的患者,会发现牙槽又高又窄。乳牙换掉后,在咬合方向上会形成牙槽形状(图 1)。
但是,对于伴有乳牙发育不全的患者,局部生长潜力降低导致牙槽实际缺损,进而影响下颌外观和形状。