-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
解剖位置
Key points
- 如果上颌骨量不足,应考虑使用颧骨、翼状骨和犁骨来加强固定
- 在手术中使用适当的诊断工具来确定相关解剖区域
- 舌皮层穿孔所致的舌下结构损伤可引发出血和致命的并发症
¨
一般注意事项
口腔种植体通常在下颌骨和上颌骨中植入,有时也在颧骨、翼状骨或犁骨等其他骨结构中植入。
为了确定相关的解剖结构,使用充分的影像技术进行解剖结构的诊断评估至关重要。CT 影像可提供骨密度和皮质水平的相关信息。临床医师应考虑不同解剖区域的典型骨质。
上颌和面中部
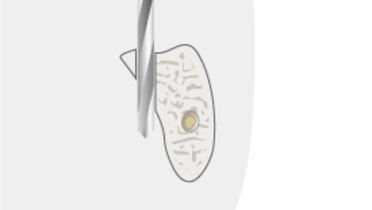
上颌骨及其结节通常为松质结构。应考虑为较松骨质专门设计的种植体和牙钻方案(如准备骨孔)。鼻窦皮质骨可用于加强(双重皮质)种植体固定。虽然只要鼻窦在临床检查和放射检查中结果正常且无鼻窦炎迹象就可以进行手术,但仍应尽量避免鼻窦穿孔。
如果上颌骨量(非常)少,应考虑使用 颧骨、 翼状蝶骨 或鼻下区域/犁骨。应避免鼻腔穿孔。只要提高鼻粘膜且未造成穿孔,就可以使用双重皮质固定。鼻腭神经损伤会影响前牙区中敏感的神经分布区域。
下颌
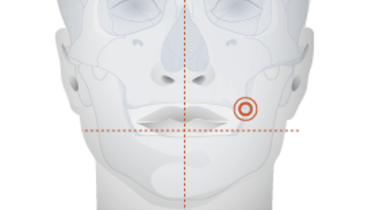
下颌骨通常为硬质骨/皮质骨结构,颌孔间区域尤其如此。应考虑为硬质骨骼专门设计的种植体形状和牙钻方案(如使用攻丝钻)。保护下牙槽和颏神经至关重要。损伤甚至压迫这些神经会导致(永久性)感觉错乱、触觉减退或感觉缺失。 因此,应使用必需的诊断工具,确保下颌管、骨孔和种植体之间保持足够距离 — 最少为 1 mm。必须注意颏神经的具体位置和前牙环绕。
对于每例萎缩性下颌病例,应了解断裂的潜在风险。如果在残留嵴中央植入种植体,下颌骨最小高度和宽度应为 ± 6 mm,确保达到种植体周围骨骼的最小厚度 ± 1 mm。在下颌中,需要特别注意下颌舌骨肌线下的舌骨凹部。骨骼穿孔可导致舌下络脉损伤,引发大出血和口底升高。虽然出现的机率很低,但气道阻塞是一种致命并发症。