-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
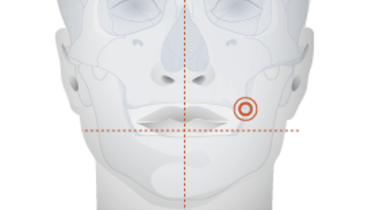
Anatomical location
Key points
- In case of limited bone volume in the maxilla consider using the zygomatic, pterygoid and vomer bone for additional anchorage
- Use appropriate diagnostic tools to identify relevant anatomical areas during surgery
- Damage of sublingual structures by perforating the lingual cortex may lead to considerable hemorrhage and fatal complications
¨
General considerations
Oral implants are usually placed in the mandibular and maxillary bone and sometimes in additional bone structures such as the zygomatic, pterygoid or vomer bone.
In order to identify relevant anatomical structures, diagnostic evaluation of the anatomical structures with adequate imaging techniques is critical. CT imaging can provide information about the bone density and degree of corticalisation. Clinicians should consider the typical bone quality associated with different anatomical areas.
Maxilla and midface
Maxillary bone and its tuberosity usually has a soft / spongeous structure. Here, implants and drill protocols designed for soft bone (for example by underpreparing osteotomy) should be considered. The cortical bone of the sinus can be used for additional (bicortical) implant anchorage. Perforation of the sinus should ideally be avoided, although acceptable as long as the sinuses seem clinically and radiologically healthy with no signs of sinusitis.
In case of (very) limited maxillary bone volume, consider additional use of the zygomatic bone, the pterygoid process of the sphenoid or the subnasal area/vomer bone. Penetration of the nasal cavity should be avoided. Bicortical anchorage is possible as long as the nasal mucosa is lifted and not perforated. Damage to the nasopalatine nerve can compromise the sensitive innervation area in the anterior zone.
Mandible
Mandibular bone usually has a dense / corticalized structure, especially in the interforaminal zone. Here, implant geometries and drill protocols designed for dense bone (for example use of screw-tap) should be considered. Protection of the inferior alveolar and the mental nerve is of paramount importance. Damage or even compression of these nerves can lead to (permanent) paresthesia, hypoesthesia or anesthesia.
Therefore, utilize the necessary diagnostic tools to ensure an adequate distance - minimum of 1 mm is essential - between the mandibular canal and the osteotomy and implant. Attention must be paid to the specific location and anterior loop of the mental nerve.
In very atrophic mandibles, the potential risk of fracture should be understood. Minimal mandibular bone height and width should be ± 6 mm to ensure a minimal peri-implant bone thickness ± of 1 mm if the implant is placed in the center of the residual ridge. Of special concern in the mandible is the lingual bone concavity below the mylohyoid line. Perforation of this osseous balcony can lead to damage of sublingual vessels causing intense hemorrhage and elevation of the mouth floor. Although rare, subsequent airway obstruction can be a fatal complication.