-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient Demand
- 0.2 Anatomical location
-
0.3
Patient History
- 2.1 General patient history
- 2.2 Local history
-
0.4
Risk Assessment
- 3.1 Risk Assessment Overview
- 3.2 Age
- 3.3 Patient Compliance
- 3.4 Smoking
- 3.5 Drug Abuse
- 3.6 Recreational Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- 3.7 Condition of Natural Teeth
- 3.8 Parafunctions
- 3.9 Diabetes
- 3.10 Anticoagulants
- 3.11 Osteoporosis
- 3.12 Bisphosphonates
- 3.13 MRONJ
- 3.14 Steroids
- 3.15 Radiotherapy
- 3.16 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
2
Treatment Options
-
2.1
Treatment planning
- 0.1 Non-implant based treatment options
- 0.2 Treatment planning conventional, model based, non-guided, semi-guided
- 0.3 Digital treatment planning
- 0.4 NobelClinician and digital workflow
- 0.5 Implant position considerations overview
- 0.6 Soft tissue condition and morphology
- 0.7 Site development, soft tissue management
- 0.8 Hard tissue and bone quality
- 0.9 Site development, hard tissue management
- 0.10 Time to function
- 0.11 Submerged vs non-submerged
- 0.12 Healed or fresh extraction socket
- 0.13 Screw-retained vs. cement-retained
- 0.14 Angulated Screw Channel system (ASC)
- 2.2 Treatment options esthetic zone
- 2.3 Treatment options posterior zone
- 2.4 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
2.1
Treatment planning
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
- 0.1 Anesthesia
- 0.2 peri-operative care
- 0.3 Flap- or flapless
- 0.4 Non-guided protocol
- 0.5 Semi-guided protocol
- 0.6 Guided protocol overview
- 0.7 Guided protocol NobelGuide
- 0.8 Parallel implant placement considerations
- 0.9 Tapered implant placement considerations
- 0.10 3D implant position
- 0.11 Implant insertion torque
- 0.12 Intra-operative complications
- 0.13 Impression procedures, digital impressions, intraoral scanning
- 3.2 Treatment procedures esthetic zone surgical
- 3.3 Treatment procedures esthetic zone prosthetic
- 3.4 Treatment procedures posterior zone surgical
- 3.5 Treatment procedures posterior zone prosthetic
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
-
4
Aftercare
単独歯を効率的に修復するモデルケース(STEM)
Key points
- 局所条件:外傷/骨折、歯根の外部/内部吸収、虫歯の進行/歯周病により単独歯の抜歯が必要な患者。
- 患者の全身/局所症状、臨床およびX線写真における感染の兆候、隣接歯の状態、患者の希望/期待を考慮してください。
- 抜歯後に歯槽骨の壁が無傷であり、感染が排除され、インプラント埋入の標準的前提条件が揃っている場合、STEM、つまり抜歯後のインプラントの即時埋入および即時負荷を検討してください。
評価/診断
口腔衛生、隣接歯の健康状態(虫歯の活動性病変、過去の修復治療、歯周状態)およびその他の口腔組織(残っている歯槽骨量、歯槽骨内の病理、粘膜状態)に特別な注意を払う必要があります。
患者様は何を期待しているでしょうか?
患者様の年齢および手術を行う最善の時期を検討してください。大多数の外傷症例は若者であり、十分に成長しておらず、咬合が安定していません。生涯の治療の前に、治療戦略を決定してくだい。
治療に関する検討事項/手順
シングルインプラント治療の標準的要件、つまり、歯槽骨の十分な寸法、手順においてあらゆる感染を排除できること、隣接歯が良好な状態にあること、顎の成長が完了していること等、が満たされる場合、STEMを勧められる可能性があります。STEMは、手術が1回のみの、円滑でより短期間での治療を意味します。
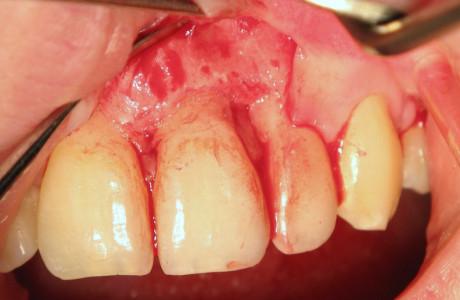
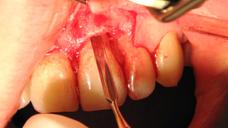
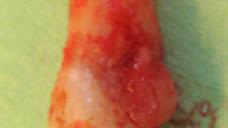
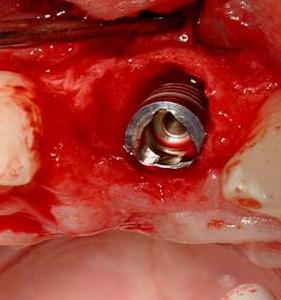
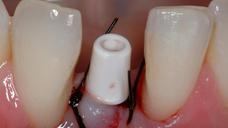
- 顎骨維持を目的とした抜歯(図1~5)
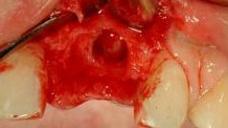
- 歯槽の入念な検査、感染の兆候として肉芽組織の除去を行います
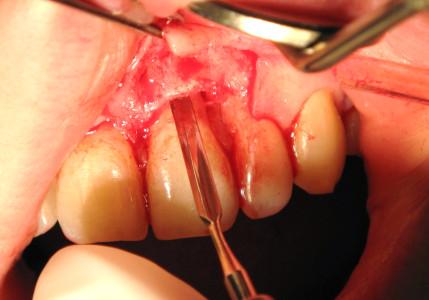
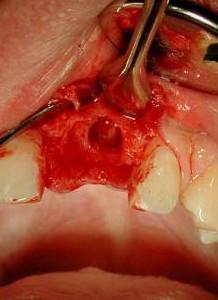
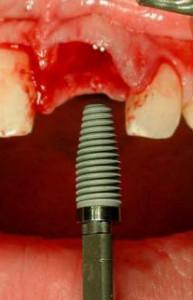
- インプラントの初期固定のため、サイトプレパレーションを歯槽の先端方向に広げます。
- 一回法外科手術に関しては、インプラント埋入トルク≥30 Ncm、または共振周波数値≥ 60 ISQ (インプラント安定指数)を目標とします
- インプラント周囲と歯槽の骨壁との間の間隙をすべて埋めます(図6、7)。自家骨/ウシの小片/代用骨材料の使用が考えられます
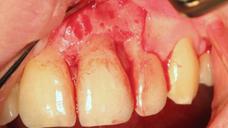
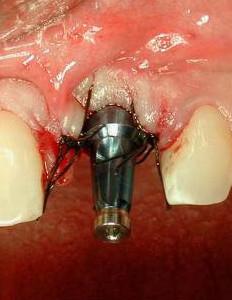
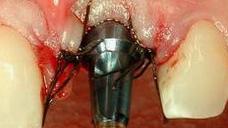
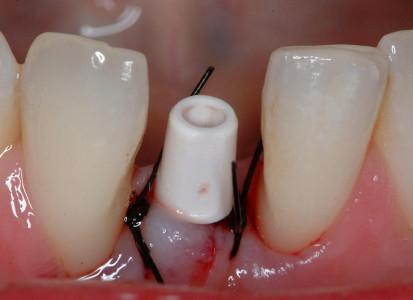
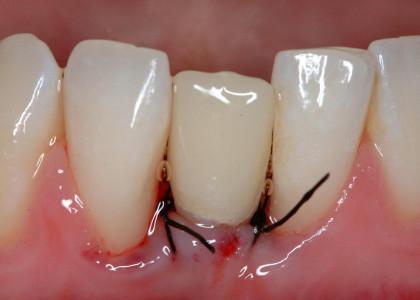
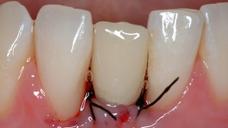
アバットメントと創傷閉鎖を結合します。プロビジョナル・クランを装着し、咬合不良を調整します(図8~11)

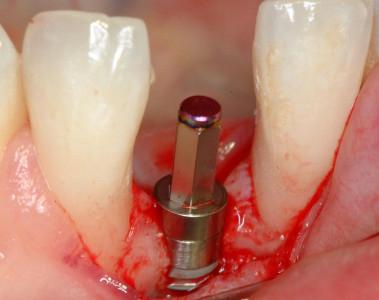
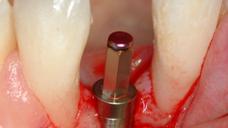
図 1
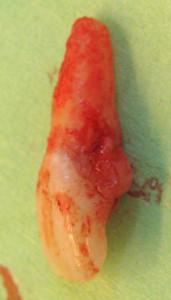
図1~4:歯根の外部/内部吸収を呈する歯21 (#9 UNIV)(矢印)。
骨維持のため、ペリオトーム器具を使用して慎重に抜歯。
図5~8:損傷がない状態の骨壁、インプラントの即時埋入、歯根サイズとインプラント径の不一致、
即時にプロビジョナルクラウンを装着するためにアバットメントを装着 。
図9~11:天然歯41 (#25 UNIV)の抜歯後、インプラント/アバットメントおよび即時のプロビジョナルクラウンを装着(咬合不良)
Digital Textbooks
Over the past 20 years there have been significant changes from the original Brånemark implant treatment protocols. Perhaps foremost has been immediate implant placement at the time of extraction which has become a viable treatment method. In addition, barrier membranes and grafting materials have been successfully used in conjunction with the immediate placement to augment extraction sockets and bony defects adjacent to immediately-placed implants.
Questions
ログインまたはご登録してコメントを投稿してください。
質問する
ログインまたは、無料でご登録して続行してください
You have reached the limit of content accessible without log in or this content requires log in. Log in or sign up now to get unlimited access to all FOR online resources.
FORウェブサイトにご登録していただきますと、すべてのオンライン・リソースに無制限にアクセスできます。FORウェブサイトへのご登録は無料となっております。