-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient Demand
- 0.2 Anatomical location
-
0.3
Patient History
- 2.1 General patient history
- 2.2 Local history
-
0.4
Risk Assessment
- 3.1 Risk Assessment Overview
- 3.2 Age
- 3.3 Patient Compliance
- 3.4 Smoking
- 3.5 Drug Abuse
- 3.6 Recreational Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- 3.7 Condition of Natural Teeth
- 3.8 Parafunctions
- 3.9 Diabetes
- 3.10 Anticoagulants
- 3.11 Osteoporosis
- 3.12 Bisphosphonates
- 3.13 MRONJ
- 3.14 Steroids
- 3.15 Radiotherapy
- 3.16 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
2
Treatment Options
-
2.1
Treatment planning
- 0.1 Non-implant based treatment options
- 0.2 Treatment planning conventional, model based, non-guided, semi-guided
- 0.3 Digital treatment planning
- 0.4 NobelClinician and digital workflow
- 0.5 Implant position considerations overview
- 0.6 Soft tissue condition and morphology
- 0.7 Site development, soft tissue management
- 0.8 Hard tissue and bone quality
- 0.9 Site development, hard tissue management
- 0.10 Time to function
- 0.11 Submerged vs non-submerged
- 0.12 Healed or fresh extraction socket
- 0.13 Screw-retained vs. cement-retained
- 0.14 Angulated Screw Channel system (ASC)
- 2.2 Treatment options esthetic zone
- 2.3 Treatment options posterior zone
- 2.4 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
2.1
Treatment planning
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
- 0.1 Anesthesia
- 0.2 peri-operative care
- 0.3 Flap- or flapless
- 0.4 Non-guided protocol
- 0.5 Semi-guided protocol
- 0.6 Guided protocol overview
- 0.7 Guided protocol NobelGuide
- 0.8 Parallel implant placement considerations
- 0.9 Tapered implant placement considerations
- 0.10 3D implant position
- 0.11 Implant insertion torque
- 0.12 Intra-operative complications
- 0.13 Impression procedures, digital impressions, intraoral scanning
- 3.2 Treatment procedures esthetic zone surgical
- 3.3 Treatment procedures esthetic zone prosthetic
- 3.4 Treatment procedures posterior zone surgical
- 3.5 Treatment procedures posterior zone prosthetic
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
-
4
Aftercare
Temporo-mandibular disorders (TMD)
Key points
- TMD is a collective term describing a group of musculoskeletal conditions affecting the temporo-mandibular joint area.
- A missing single-tooth may cause tooth movements, which in turn may induce grinding.
- A missing single-tooth replaced with a controlled precision-made implant-supported crown may rarely, if ever, cause TMJ dysfunction.
Temporo-mandibular disorders (TMD)
Routine evaluation of a patient’s temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) function is an integral part of any oral examination.
Moreover, good muscular control and painless coordination of jaw movements are desirable. A compromised ability or outright inability to perform clinically-guided or requested movements may require treatment.
TMD is a collective term describing a group of musculoskeletal conditions and/or pain sensations affecting the temporomandibular joint area. These include muscular conditions such as myofascial pain, disorders affecting the joint complex such as disc displacement and the less common arthritic diseases. Possible symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness in the muscles of mastication and the TMJs
- Joint sounds during condylar movements
- Limitations of mandibular movement
Their etiology remains controversial and unclear. One should always keep in mind that besides dental therapy, functional education, medication, physiotherapy, occlusal splints, neuroreflexotherapy and psychological counseling have all shown their merits when dealing with TMD. The dentist should not hesitate to refer the patient.
The prosthodontic intervention alone can only rarely be a specific therapy for a TMD. Guidelines are summarized in the official scientific information statement published by the American Dental Association.
They include patient education and reassurance about the benign nature of the condition, self-care, short-term pharmacotherapy (e.g. muscle relaxants), physical modalities as well as cognitive and behavioral intervention (e.g. relaxation techniques, soft foods).
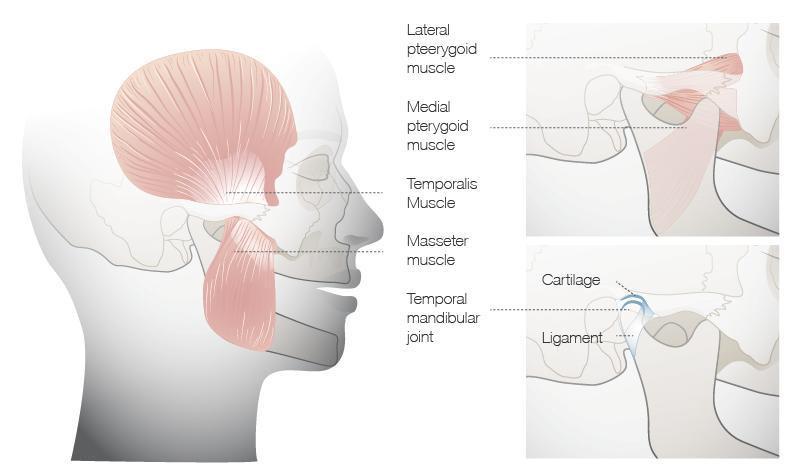
Figure 1: TMJ and attached muscles
Occlusal analysis
occlusal analysis clinical and check list ? Thank you
occlusal analysis clinical and check list ? Thank you
In reply to Occlusal analysis by Anonymous
Moderator's response:
We recommend to review the treatment guidelines for esthetic and functional check and occlusion check.