-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient Demand
- 0.2 Anatomical location
-
0.3
Patient History
- 2.1 General patient history
- 2.2 Local history
-
0.4
Risk Assessment
- 3.1 Risk Assessment Overview
- 3.2 Age
- 3.3 Patient Compliance
- 3.4 Smoking
- 3.5 Drug Abuse
- 3.6 Recreational Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- 3.7 Condition of Natural Teeth
- 3.8 Parafunctions
- 3.9 Diabetes
- 3.10 Anticoagulants
- 3.11 Osteoporosis
- 3.12 Bisphosphonates
- 3.13 MRONJ
- 3.14 Steroids
- 3.15 Radiotherapy
- 3.16 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
2
Treatment Options
-
2.1
Treatment planning
- 0.1 Non-implant based treatment options
- 0.2 Treatment planning conventional, model based, non-guided, semi-guided
- 0.3 Digital treatment planning
- 0.4 NobelClinician and digital workflow
- 0.5 Implant position considerations overview
- 0.6 Soft tissue condition and morphology
- 0.7 Site development, soft tissue management
- 0.8 Hard tissue and bone quality
- 0.9 Site development, hard tissue management
- 0.10 Time to function
- 0.11 Submerged vs non-submerged
- 0.12 Healed or fresh extraction socket
- 0.13 Screw-retained vs. cement-retained
- 0.14 Angulated Screw Channel system (ASC)
- 2.2 Treatment options esthetic zone
- 2.3 Treatment options posterior zone
- 2.4 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
2.1
Treatment planning
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
- 0.1 Anesthesia
- 0.2 peri-operative care
- 0.3 Flap- or flapless
- 0.4 Non-guided protocol
- 0.5 Semi-guided protocol
- 0.6 Guided protocol overview
- 0.7 Guided protocol NobelGuide
- 0.8 Parallel implant placement considerations
- 0.9 Tapered implant placement considerations
- 0.10 3D implant position
- 0.11 Implant insertion torque
- 0.12 Intra-operative complications
- 0.13 Impression procedures, digital impressions, intraoral scanning
- 3.2 Treatment procedures esthetic zone surgical
- 3.3 Treatment procedures esthetic zone prosthetic
- 3.4 Treatment procedures posterior zone surgical
- 3.5 Treatment procedures posterior zone prosthetic
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
-
4
Aftercare
顎関節症(TMD)
Key points
- TMDは、顎関節領域に影響を及ぼす筋骨格系の異常の総称です。
- 欠損歯があると、歯の動揺を引き起こす可能性があり、グラインディングを引き起こすおそれもあります。
- 単独歯欠損部を適切かつ精密に作製したインプラント支持クラウンで修復した場合、顎関節機能不全を引き起こすことは滅多にありません。
顎関節症(TMD)
いずれの口腔検査でも、顎関節(TMJ)機能の評価は不可欠です。
また、顎運動時の筋制御が良好で、痛みを生じることなく協調するのが理想的です。臨床的に誘導または要求される運動を行うことが困難な場合は、治療が必要です。
TMDは、顎関節領域に影響を及ぼす筋骨格系の異常または疼痛の総称であり、筋筋膜性疼痛のような筋疾患、関節円盤転位のような関節複合体の障害、あるいは関節性疾患等が含まれます。TMDの症状には次のようなものがあります。
- 咀嚼筋およびTMJの疼痛または圧痛
- 顆頭運動時の関節音
- 下顎の運動制限
TMDの成因に関しては議論の余地があり、未だ明かではありません。TMDを治療する際は、歯科治療以外にも、機能訓練、投薬、スプリント、神経反射療法および心理カウンセリングが有益であることが報告されていますので、ためらわずに専門医に紹介するべきです。
補綴治療単独では、TMDの特効治療となることは稀です。米国歯科医師会の公式の学術情報声明のなかに、ガイドラインが要約されています。
このガイドラインには、本疾患が良性であることを患者に説明し、安心させることをはじめ、セルフケア、短期的薬物療法(筋弛緩薬等)、物理療法および認知・行動療法(リラクゼーション法、柔らかい食物等)等の有効な方法が記載されています。
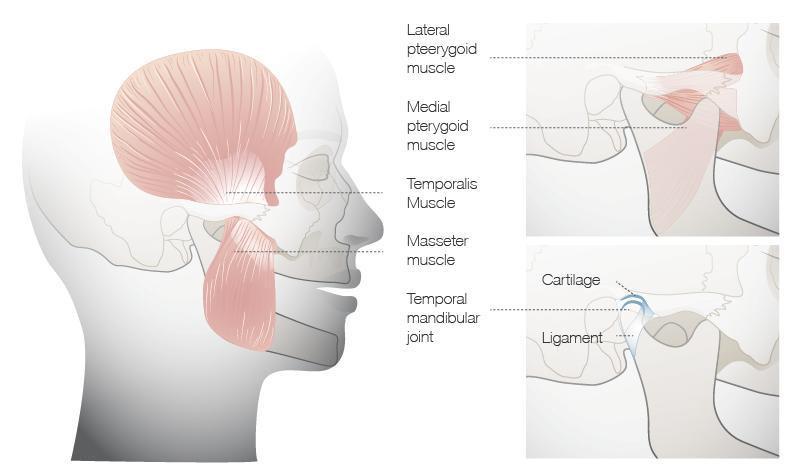
図1: TMJと付着筋
Digital Textbooks
Biomechanical studies of the relationship between and cranial form and function have frequently appeared in dental and engineering literature since the mid-to-late 90s. It is known that deformation of the cranial vault occurs during contraction of the temporalis muscle, most particularly the anterior portion of the muscle. Craniofacial osseous stress and strain occurring during mastication is moderated by the unique, complex suture types found throughout the skull.
Questions
ログインまたはご登録してコメントを投稿してください。
質問する
ログインまたは、無料でご登録して続行してください
You have reached the limit of content accessible without log in or this content requires log in. Log in or sign up now to get unlimited access to all FOR online resources.
FORウェブサイトにご登録していただきますと、すべてのオンライン・リソースに無制限にアクセスできます。FORウェブサイトへのご登録は無料となっております。
Occlusal analysis
occlusal analysis clinical and check list ? Thank you
occlusal analysis clinical and check list ? Thank you
In reply to Occlusal analysis by 匿名
Moderator's response:
We recommend to review the treatment guidelines for esthetic and functional check and occlusion check.