-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
Grafting, maxilla
Key points
- The atrophic edentulous upper jaw presenting with less than 5-6 mm in height and 6 mm in width, requires bone augmentation prior to implant placement
- In the anterior region autologous bone block grafts are used for vertical and horizontal bone augmentation
- In the posterior maxilla the sinus lift is the procedure of choice for vertical bone augmentation
- Sinus floor augmentation can be performed with immediate or delayed implant placement
- Anorganic bovine bone substitute materials are as effective as autogenous bone for sinus floor augmentation
Indications
In the edentulous upper jaw implant insertion can be limited due to the adjacent anatomical structures (nasal floor, maxillary sinus). Less than 5-6 mm in height and 6 mm in width requires augmentation before implant placement.
Anterior Maxilla
In the anterior maxilla autologous bone block grafting for vertical and/or horizontal bone augmentation is the treatment of choice (Fig 1). As an alternative, allogenic bone blocks are in the focus of interest, but their usage is presently not recommended due to limited evidence. After alveolar ridge grafting a healing period of 4-6 months is recommended and implants are placed in a second stage surgery.
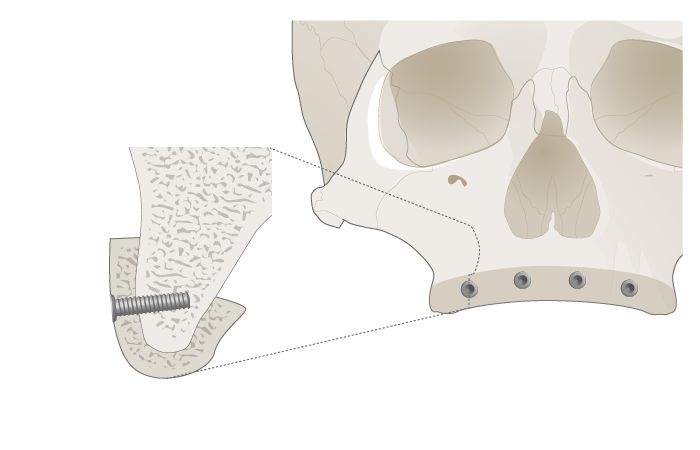
Posterior Maxilla
In the posterior maxilla the augmentation technique is based on the elevation of the sinus membrane from the maxillary sinus floor and grafting of the basal maxillary sinus. Sinus floor augmentation can be performed as a one- or two-stage approach with simultaneous or delayed implant placement depending on the primary implant stability. With a residual alveolar bone height of ≥3-4 mm implants are inserted simultaneously with sinus grafting. A two-step procedure is recommended in cases of less than 4 mm where sufficient primary implant stability is not likely to be achieved. A delayed implant insertion is then performed after 4-6 months of healing.
Loading of the implants inserted in the augmented sinus is recommended after 4-6 months.
Bone substitute
For maxillary sinus grafting, particulated materials are used due to their superior integration properties compared to block-shaped grafts. Multiple particulated bone substitute materials and/or autologous bone grafts are available (Fig 2). Anorganic bovine bone substitutes (ABB) are comparable to particulated autologous bone in terms of implant survival and newly formed bone. Importantly Anorganic Bovine Bone is considered to be a non-resorbable bone substitute, forming a composite with newly formed bone and therefore may reduce bone resorption processes over time and guarantee long-term implant stability. The available data does not prove the superiority of the different techniques proposed for sinus lifting.
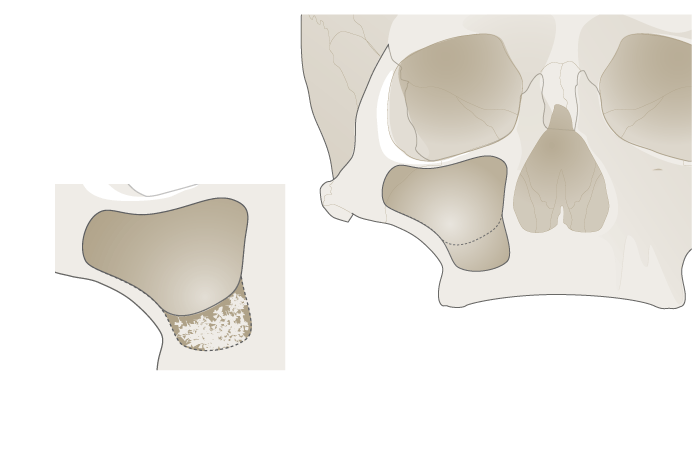

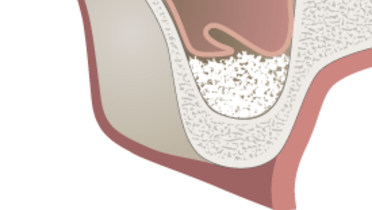


Can you help?
My mom is a healthy 64 year old woman. She is and upper edentulous patient who needs a sinus lift and needs horizontal and vertical BRG in the anterior region. How do I find some one who can do this correctly? I also know it is expensive and I would love to try and pay for it because it would be like her winning the lottery.?
My mom is a healthy 64 year old woman. She is and upper edentulous patient who needs a sinus lift and needs horizontal and vertical BRG in the anterior region. How do I find some one who can do this correctly? I also know it is expensive and I would love to try and pay for it because it would be like her winning the lottery.?