-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
种植体植入(上颌)
Key points
- 解剖学相关结构被破坏的风险有限
- 如果可以保证适当的骨量和骨质且种植体呈前后分布,则植入 4 个种植体就已足够
- 需要考虑患者的年龄和灵活性、偏好、美观效果以及上颌间前后关系,以决定选择固定修复体还是可摘覆盖义齿
- 当患者的唇线较高时,美齿效果往往是主要考量因素
切口
切口可以开在牙槽嵴顶部或远端唇褶上。这两种方法的效果看起来不相上下。中间线处的矢状面松弛切口便于实现唇部粘膜骨膜反射。合理的做法是,尽量争取使种植体的唇侧和腭侧都存在角质化组织。
切断鼻腭神经血管束很少会让患者感觉到由此造成的腭粘膜麻木感。这种麻木感通常会在数周后消失。当上颌骨量有限时,有几位作者清空了鼻腭管并用自体骨进行移植。他们获得了良好的结果。种植体很少植入到过于偏后的位置,以免接触腭神经血管束。
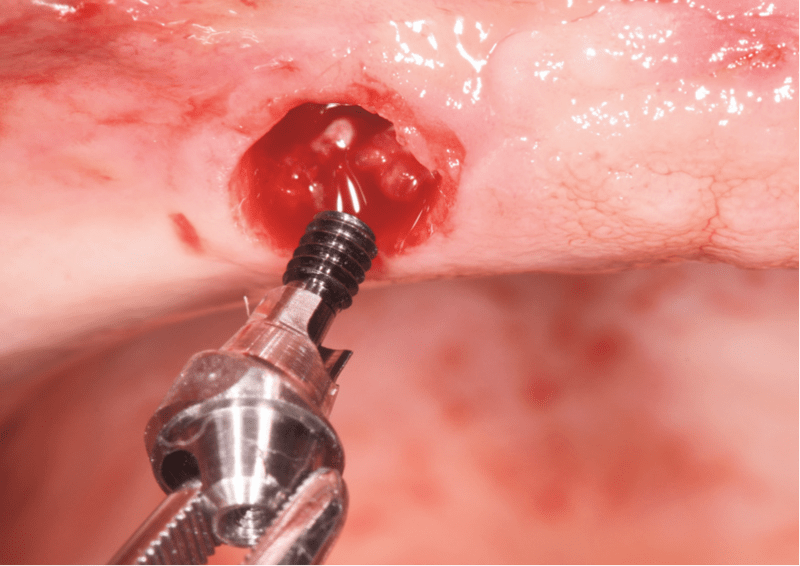
初期稳定性注意事项
即使骨矿化不足,使钻孔的尺寸偏小仍然可实现良好的初期稳定性。初期稳定性通过测量种植体植入扭矩和/或牙动度和/或进行共振频率分析 (RFA) 来评估,可据此选择即刻负重或延期负重方案。以前,在上颌中植入车削面种植体需遵守 6 个月愈合期的原则。
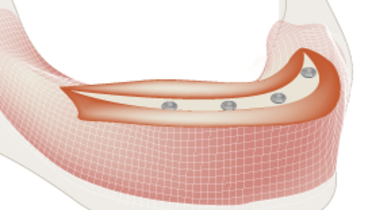
前后分布及种植体倾斜
从生物力学上讲,最好是实现较大的前后分布跨度。远端种植体可以向背侧倾斜,与上颌窦前壁保持平行。对于后一种情况,使用角度式基台可以提供最佳的修复螺丝通道。
此外,当萎缩上颌的唇部倾斜导致种植体前倾时,可以通过复合基台来弥补,从而实现适当的平行度(见图)。这类倾斜种植体的成活率与轴向种植体相仿。
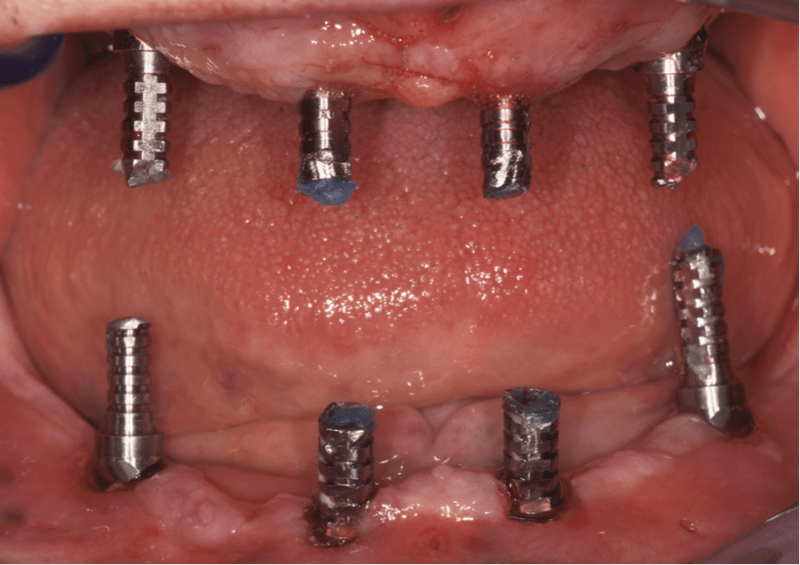
正面区域种植体开窗术较为常用,似乎不会引发问题。
种植体数目及修复类型注意事项
当患者的唇线较高且选择固定修复体作为治疗方案时,该方案有助于使种植体集中于背侧部位,以便为负责实施修复的牙医提供更高的正面区域操作自由度。
关于上颌中支撑固定式完整修复体所需的最佳种植体数目,目前尚无一致意见:4 个种植体已能够提供较高的可预测性。平均来说,临床医师往往会植入 6 个种植体。可能有必要针对重度上颌骨萎缩的情况行鼻底或窦提升术。
当患者无法负担固定式修复体的费用时、当上颌间关系为 III 类时,或无论何时缺少足够的骨量来支撑相应位置需要植入的种植体数目时,首选杆卡固定的覆盖义齿。如果上颌萎缩情况为中度,则使用非夹板固定种植体可收到令人满意的效果。