-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient Demand
- 0.2 Anatomical location
-
0.3
Patient History
- 2.1 General patient history
- 2.2 Local history
-
0.4
Risk Assessment
- 3.1 Risk Assessment Overview
- 3.2 Age
- 3.3 Patient Compliance
- 3.4 Smoking
- 3.5 Drug Abuse
- 3.6 Recreational Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- 3.7 Condition of Natural Teeth
- 3.8 Parafunctions
- 3.9 Diabetes
- 3.10 Anticoagulants
- 3.11 Osteoporosis
- 3.12 Bisphosphonates
- 3.13 MRONJ
- 3.14 Steroids
- 3.15 Radiotherapy
- 3.16 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
2
Treatment Options
-
2.1
Treatment planning
- 0.1 Non-implant based treatment options
- 0.2 Treatment planning conventional, model based, non-guided, semi-guided
- 0.3 Digital treatment planning
- 0.4 NobelClinician and digital workflow
- 0.5 Implant position considerations overview
- 0.6 Soft tissue condition and morphology
- 0.7 Site development, soft tissue management
- 0.8 Hard tissue and bone quality
- 0.9 Site development, hard tissue management
- 0.10 Time to function
- 0.11 Submerged vs non-submerged
- 0.12 Healed or fresh extraction socket
- 0.13 Screw-retained vs. cement-retained
- 0.14 Angulated Screw Channel system (ASC)
- 2.2 Treatment options esthetic zone
- 2.3 Treatment options posterior zone
- 2.4 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
2.1
Treatment planning
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
- 0.1 Anesthesia
- 0.2 peri-operative care
- 0.3 Flap- or flapless
- 0.4 Non-guided protocol
- 0.5 Semi-guided protocol
- 0.6 Guided protocol overview
- 0.7 Guided protocol NobelGuide
- 0.8 Parallel implant placement considerations
- 0.9 Tapered implant placement considerations
- 0.10 3D implant position
- 0.11 Implant insertion torque
- 0.12 Intra-operative complications
- 0.13 Impression procedures, digital impressions, intraoral scanning
- 3.2 Treatment procedures esthetic zone surgical
- 3.3 Treatment procedures esthetic zone prosthetic
- 3.4 Treatment procedures posterior zone surgical
- 3.5 Treatment procedures posterior zone prosthetic
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
-
4
Aftercare
ポステリア・ソリューション
Key points
- ノーベルバイオケアのポステリア・ソリューションに使用する製品はノーベルバイオケア社独自のものです。
- 同システムの活用により、即時埋入および暫間補綴物の準備が整います。
- 適切な治癒後、軟組織プロファイルを獲得し、最終補綴物を最適化します。
ノーベルバイオケアのポステリア・ソリューションの開発により、予知性、審美性、機能性が高く、セメントを使用しない治療法を選択して臼歯部歯列を修復することが可能です。システムを構成する製品は、ノーベルアクティブWP (ワイド・プラットフォーム)インプラント、解剖学的構造のテンポラリーおよびヒーリング・アバットメント、フルカントゥア ジルコニア(FCZ)、角度付きスクリューチャネル(ASC)とオムニグリップ・ツールです。ノーベルクリニシャンの3Dデジタル治療計画作成と連携させることにより、インプラント埋入が最適化されます。
ポステリア・ソリューションは、理想的に臼歯部を修復するためのもので、ノーベルアクティブWPインプラントには、多くの利点があります。アクティブインプラントのスレッドデザインは、高いトルク値(最大70Ncm)でのインプラントの固定が適用できます。プラットフォーム・シフティングは、軟組織の良好な反応を高め、また骨の高さをインプラントの最も冠状側の面に維持する可能性があります。ワイド・プラットフォーム・インプラントにより、臼歯根形態の解剖学的要件に対処します。形状およびスレッドデザインは、抜歯窩への即時埋入(および暫間補綴物の装着)を実現します。
デジタル治療計画作成(ノーベルクリニシャン)およびガイデッドサージェリー(ノーベルガイド)による埋入を採用することにより、インプラント埋入は軟・硬組織プロファイルを最大化し、理想的な修復結果をもたらします。
インプラントを埋入した後、テンポラリー・アバットメントを装着し、それに暫間補綴物を装着することができます。こうすることにより、臨床医は、最終補綴物を形成し、自然歯の歯根形態およびエマージェンス・プロファイルを再現することが可能となります。骨結合の段階が完了すると、インプラントおよび軟組織の印象採得に理想的な環境が整います。暫間補綴物を取り外し、インプラントレベルの印象を採得します(オープントレーまたはクローズドトレーが選択可能です)。
最終補綴物は、フルカントゥア・ジルコニアにより作製します。築盛材のポーセレンを使用する必要がないため、全体の強度を高め、チッピングのリスクを解消します。インプラントの埋入角度が理想的ではない場合においても、アクセスホールの角度を最大25°まで調整することが可能です。
このように、ポステリア・ソリューションにより、予知性、審美性、機能性が高く、スクリュー固定式の優れた補綴物が患者に装着され、長年にわたり使用されることになります。
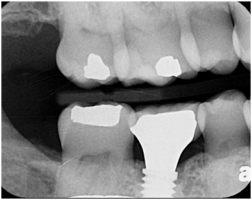
図1:プラットフォーム上に骨があるプラットフォーム・スイッチの例
Digital Textbooks
In fact, some molar spaces have a 12.0 mm mesiodistal dimension and, therefore, with a 4.0 mm diameter implant even a well-contoured crown will reach the limits of the recommended lateral extension.
Additionally, if the implant is not centered beneath the restoration’s occlusal surface, the occlusal loading forces can be greater and may overload of the abutment screw or implant.