-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
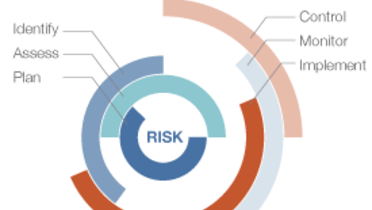
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
General health check
Key points
- During regular recall visits update information on general health of patient, such as infection or treatments in the head and neck area
- Update patient medication status
- In case of doubt enquire at patient’s family doctor or specialists
Recall visit - General health check update
Patient health can change considerably over time - therefore at every recall visit, check and get updated information on general health of patient, and if needed adapt maintenance policy adequately. Information (for example a poster) concerning this topic in the waiting room is helpful. Not only the clinician should ask the patient, but also the staff should be aware of the importance of these updates.
Questioning should always consider: systemic, cardio-vascular, blood, neural, gastro-intestinal, urogenital and metabolic diseases, surgeries and hospital visits (for example radiotherapy treatments), allergies, infections, specific infections (Hepatitis, HIV), travel to tropical countries (latency of certain diseases).
Reevaluate specifically the head and neck area: nasal or sinusal surgery, laryngeal complaints etc.
In case of critical new situations, ask for medical reports. In case of doubt always contact the treating specialist or the family doctor.
Medication update
Review medication situation and if any changes occured. Question especially all medication related the blood/heart (like anticoagulants) or the bone (bisphosphonates). Elderly patients consider medication a routine and might forget to mention them, if asked in a generic way.