-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient Demand
- 0.2 Anatomical location
-
0.3
Patient History
- 2.1 General patient history
- 2.2 Local history
-
0.4
Risk Assessment
- 3.1 Risk Assessment Overview
- 3.2 Age
- 3.3 Patient Compliance
- 3.4 Smoking
- 3.5 Drug Abuse
- 3.6 Recreational Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- 3.7 Condition of Natural Teeth
- 3.8 Parafunctions
- 3.9 Diabetes
- 3.10 Anticoagulants
- 3.11 Osteoporosis
- 3.12 Bisphosphonates
- 3.13 MRONJ
- 3.14 Steroids
- 3.15 Radiotherapy
- 3.16 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
2
Treatment Options
-
2.1
Treatment planning
- 0.1 Non-implant based treatment options
- 0.2 Treatment planning conventional, model based, non-guided, semi-guided
- 0.3 Digital treatment planning
- 0.4 NobelClinician and digital workflow
- 0.5 Implant position considerations overview
- 0.6 Soft tissue condition and morphology
- 0.7 Site development, soft tissue management
- 0.8 Hard tissue and bone quality
- 0.9 Site development, hard tissue management
- 0.10 Time to function
- 0.11 Submerged vs non-submerged
- 0.12 Healed or fresh extraction socket
- 0.13 Screw-retained vs. cement-retained
- 0.14 Angulated Screw Channel system (ASC)
- 2.2 Treatment options esthetic zone
- 2.3 Treatment options posterior zone
- 2.4 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
2.1
Treatment planning
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
- 0.1 Anesthesia
- 0.2 peri-operative care
- 0.3 Flap- or flapless
- 0.4 Non-guided protocol
- 0.5 Semi-guided protocol
- 0.6 Guided protocol overview
- 0.7 Guided protocol NobelGuide
- 0.8 Parallel implant placement considerations
- 0.9 Tapered implant placement considerations
- 0.10 3D implant position
- 0.11 Implant insertion torque
- 0.12 Intra-operative complications
- 0.13 Impression procedures, digital impressions, intraoral scanning
- 3.2 Treatment procedures esthetic zone surgical
- 3.3 Treatment procedures esthetic zone prosthetic
- 3.4 Treatment procedures posterior zone surgical
- 3.5 Treatment procedures posterior zone prosthetic
-
3.1
Treatment procedures general considerations
-
4
Aftercare
Post-operative soft tissue management
Key points
- The postoperative soft tissue management can coincide with the regular control recalls.
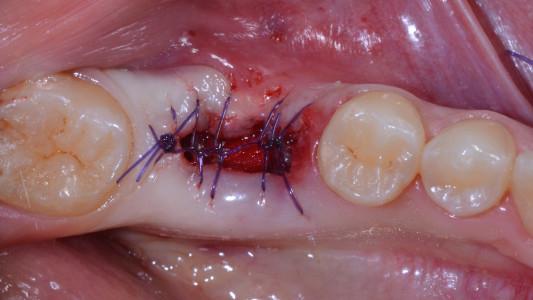
- The patient is seen one to two weeks after dental implant placement for suture removal, postsurgical instructions, and observation of healing. In case of one-stage or immediate loading protocols, soft diet is recommended for 30 days.
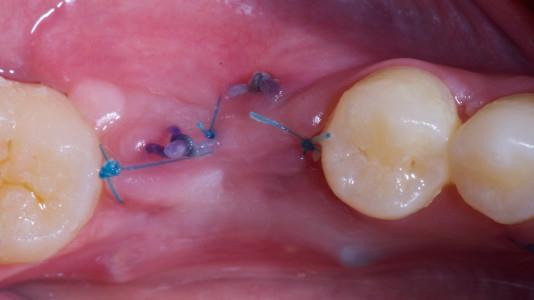
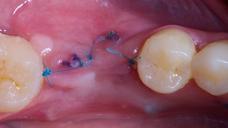
- The patients are instructed to rinse the mouth with 0.2% chlorhexidine mouthwash thrice a day without brushing the implant area until suture removal (7 to 14 days after).
- Evaluate wound healing and manage any signs of inflammation or infection.
- Patients would greatly benefit by having dental implants placed flapless, reducing the postoperative pain and consumption of analgesics.
Post operative soft tissue management - Timing
Following implant placement, patients receive oral and written recommendations about medication, oral hygiene maintenance and diet, depending on the type of surgical and prosthetic procedures.
Assessment of soft tissue during recall visits
The patients are instructed to rinse the mouth two to three times per day with an antiseptic mouth rinse with 0.2% chlorhexidine, starting the day after surgery and until suture removal (7 to 14 days after), without brushing the implant area.
Patients would greatly benefit by having dental implants placed flapless, reducing the postoperative pain and consumption of analgesics.
Similarly to the treatment of the edentulous, the patient is seen at day 1 - 3, day 7 - 14 and week for soft tissue control, management, and suture removal. In case of one-stage or immediate loading protocols, soft diet is recommended for 30 days.
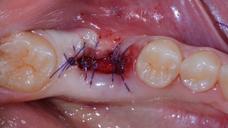
Careful attention is given to the possibility of soft tissue, hard tissue, and/or dental implant infection, particularly to detect any signs of inflammation and infection such as swelling, exudate, pain, bleeding. In case of wound dehiscence re-suture and/or additional sutures (only within 24 to 48 hours) should be used. In case of post-extractive implants, the patients should be followed until completely soft tissue coverage.
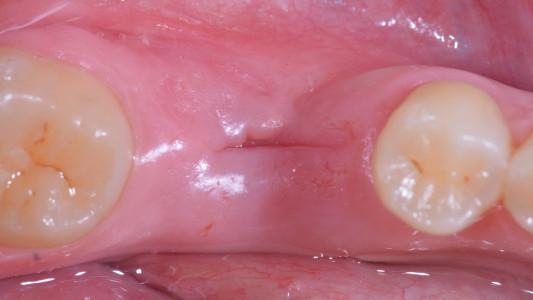
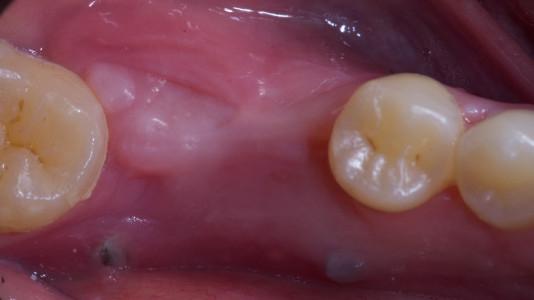
The patient is seen again six weeks post-placement with the expectation that soft-tissue healing should be complete. Plaque when present, should be removed and oral hygiene instruction should be reinforced.
At this time, oral hygiene is reviewed and a maintenance appointment is scheduled. Three months post-placement a radiograph is taken to evaluate hard-tissue levels.
Soft tissue and provisional denture fit
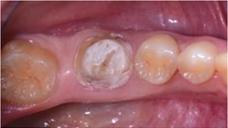
In case of immediate loading, the clinician should carefully control the fit of the provsional restoration to avoid tissue trauma. If cemented retained restoration have been apply, excessive control of the cement should be carefully and meticulous removed. Since soft tissues change during the healing, the temporary restoration should be customized accordingly. Nevertheless, it is preferable avoid any removal of the temporary restoration during the first 6-8 weeks of healing.
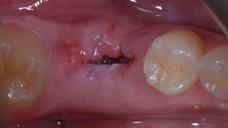
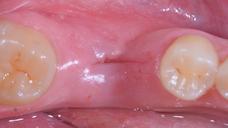
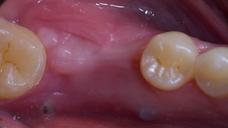
Figure 1: Pre-extaction Figure 2: Extraction Figure 3: 7 days suture removal Figure 4: 14 days
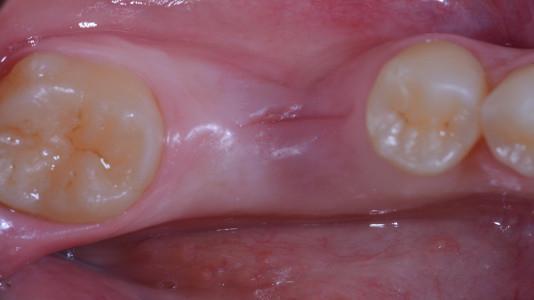
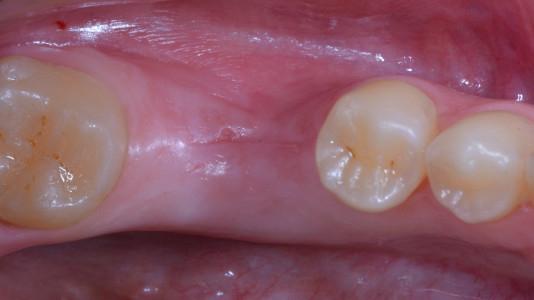
Figure 5: 3 weeks Figure 6: 6 weeks Figure 7: 7 days after implant placement (IP) and guided bone regeneration (GBR) procedure Figure 8: 14 days after IP and GBR procedure.