-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
缝线拆除
Key points
- 缝线拆除一般不需要麻醉
- 放弃对粘膜下缝线的拆除可导致异物反应、感染和最终的种植体脱落。
- 必须认真对待缝线拆除,将其视作一个重要的治疗程序
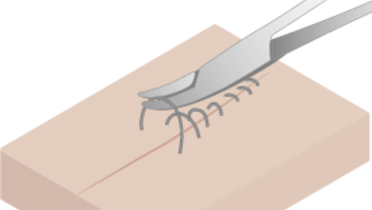
缝线拆除
根据患者的年龄和伤情程度,对粘骨膜伤口的缝线拆除应在 8 到 12 天后进行。即使是可吸收的缝线,在这段愈合时间过后拆除剩余的缝线也是有好处的。
必须清晰确定缝线,用止血钳或棉无齿镊将其向伤口处拉,用剪刀或解剖刀片在靠近粘膜处采取环切术。如果采用了间断缝合,最好先拆除两根缝线中的第一根,以验证伤口是否闭合。如果伤口还未闭合,推迟拆除余下的缝线。
在手术后缝合伤口时,记录缝针的针数是一个良好规程和行医标准 - 当拆除缝线时,将拆除的缝线针数与患者记录上所注的针数进行比较。
在缝线拆除后,用湿润的纱布将粘膜上的残屑擦拭干净会很有帮助。