-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
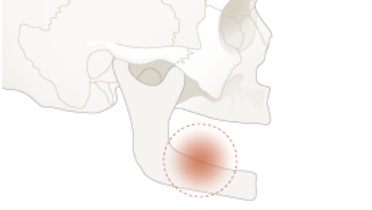
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
感染 - 微生物诊断
Key points
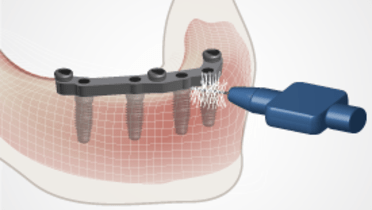
- 边缘骨缺失可导致形成深腔。双重感染可导致种植体周围炎
- 存在种植体周围炎证据时,进行微生物敏感性试验可能具有临床意义
微生物群参数
有无种植体/种植体的数量会影响缺齿患者唾液中及舌头上的需氧菌和厌氧菌种类。
种植体周围炎患者的龈下微生物群在不同的研究中有不同的报道。牙周致病菌较部分牙缺失患者少。Prevotella nigrescens、Fusobacterium nucleatum、P. gingivalis、T. forsythia、Treponema denticola 或 Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans 与种植体周围炎相关。微生物群落不同于牙周炎,消化链球菌或葡萄球菌数量较多。通常是肠道杆菌、葡萄球菌和酵母菌。
抗生素的用药选择
作为机械/手术治疗的辅助手段,全身使用抗生素对种植体周围炎的有益疗效仍未经证实。粘膜下微生物群的组成是否为治疗效果的决定性因素仍未得到证实。通过检测耐药性菌种,微生物检测有助于选择合适的抗生素。
微生物检测
适用于门诊人群的检测:
-
- 相差显微
- 培养
- 乳胶凝集试验
- 棋盘式 DNA-DNA 杂交法
- 聚合酶链反应
相差显微:
简单而快速的诊疗检测,可提供球菌/杆菌/丝状菌及运动型微生物的比例。运动型微生物的比例增加与牙周炎加重相关;对于种植体周围炎,这种关系尚未确立。
培养
培养是一种技术要求高而耗时的方法。用于确定对抗生素的敏感性。将纸尖插入种植体周袋并装入小瓶送到实验室。
乳胶凝集试验
包括涂有特异性抗体的微珠。与样品中的目标抗原接触时,微珠会结团。简单快速。
棋盘式 DNA-DNA 杂交法
适合复杂生态系统的最佳检测方法。可鉴定多个样品中的大量菌种。允许检测 ≥104 个细菌。
聚合酶链反应
需要通过引物对 DNA 序列进行扩增。如果发生扩增,则证明存在目标菌种。可检测 ≥ 10 个细菌。生物膜可能含有抑制反应的酶。