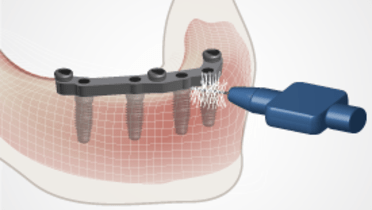
-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
Post-placement
Key points
- If prosthesis was placed on or soon after the day of implant surgery, review postoperative medications and tissue healing
- Oral hygiene instructions and periodic maintenance are important for good long term prognosis
- Oral hygiene aids might have to be modified to allow access
- If applicable, the patient is instructed to remove the opposing prosthesis at night
- Keep adjustments in the immediate post-placement period to a minimum in order to give the patient time to adapt to the new prosthesis
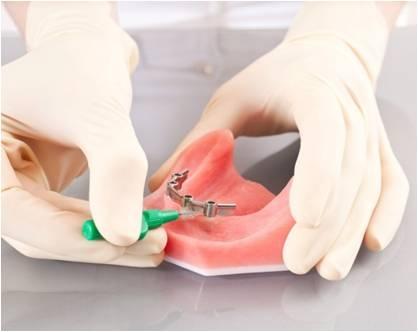
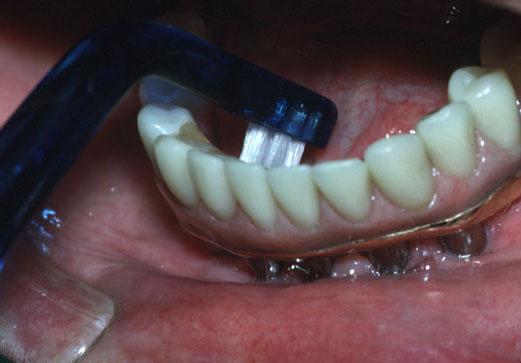
Post insertion - oral hygiene considerations
At this appointment, a careful evaluation of the patient's oral hygiene and soft tissue response is performed and adjustments made as needed.
A daily home-care program must be customized to the individual's ability to clean the oral cavity. After placement of the implants, hygiene recall visits at appropriate intervals will be needed to prevent the occurrence of an inflammatory response around implants and in the area of implant surgery.
Since maintaining good oral hygiene around fixed complete dentures is more difficult than with removable implant prostheses, oral hygiene instructions should be performed using soft (electric) toothbrushes, floss/yarn, end-tufted brushes, interproximal brushes and other aids. The oral hygienist or other auxiliaries should be involved when setting up a recall protocol.
Evaluation of esthetics, function and comfort
The patient should be interviewed to determine satisfaction with prosthesis and a careful evaluation of occlusion, speech and masticatory function made. Patient concerns should be addressed by adjustments with an understanding the presence of the new prosthesis may be such a big change that adjustments should be used at a minimum in order to give the patient time to adapt to the prosthesis.