-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
Maxillo-mandibular relations
Key points
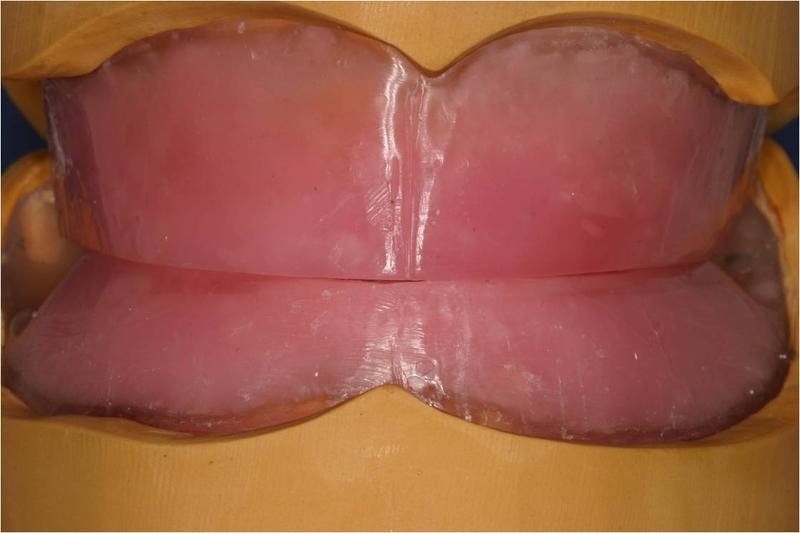
- For maxillo-mandibular relations, the occlusion rims establish the vertical dimension and delineate occlusal plane, lip line, smile line and midline
- A balanced occlusal scheme is preferred if the opposing arch has a removable prosthesis
Re-establishment of transversal and sagittal jaw relations
One goal in the treatment of the fully edentulous patient is to re-establish the maxillo-mandibular relation in the transversal and sagittal dimensions comprising adequate facial height. The occlusal contact situation between the denture teeth is defined accordingly. Prosthetic parameters have been used in the initial diagnostic and planning phase for the evaluation of old dentures and to create a tooth arrangement that depicts the final prosthetic result. This artwork is the source of information that will be transferred to the final fixed prosthesis. If the opposing arch is restored with a removable prosthesis, a balanced occlusion is recommended.
Occlusion RIMS Technique
The technique with record bases and occlusion rims fabricated on the definitive casts is still considered the gold standard to determine maxillo-mandibular relations and interocclusal registration in edentulous patients. The rims establish the vertical dimension and delineate the occlusal plane, the lip line, smile line and midline. The record bases are either mucosally-supported or existing implants may be used for retention. Stability of record bases is essential if an accurate maxillo-mandibular relation record is to be obtained. In general, mandibular record bases are less stable than maxillary record bases and, consequently, the use of existing implants to retain and stabilize a record base has greater impact in the mandible.
Recording of maxillo-mandibular relations can be performed with a variety of techniques and materials. The technique employed ideally captures a stress-free patient-dictated centric relation position. In some clinical situations, dentist-guidance of the mandible to closure in centric relation may be necessary. The ideal properties of a recording medium are that it have a short setting time, set rigid and be free flowing to offer negligible resistance upon patient closure.