-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
软组织处理
Key points
- 穿粘膜种植体周围是否需要角质化/固定软组织仍然是个争论不休的问题
- 在固定不动的情况下,种植体周围无炎症的软组织更容易维护
种植体周围软组织处理的目的
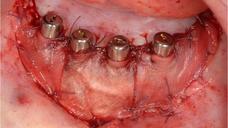
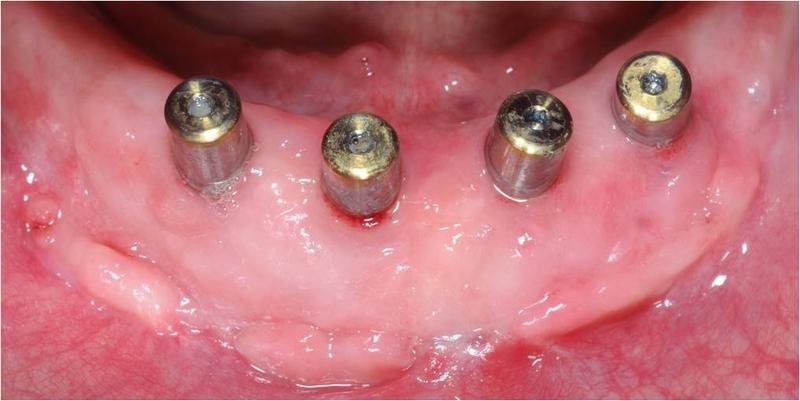
在缺齿下颌中,种植体周围软组织处理的目的是最终重建附着的牙龈或将软组织固定在种植体-软组织接触面处。前庭成形术意味着前庭的加深。
用于缺齿下颌软组织处理的技术和移植物
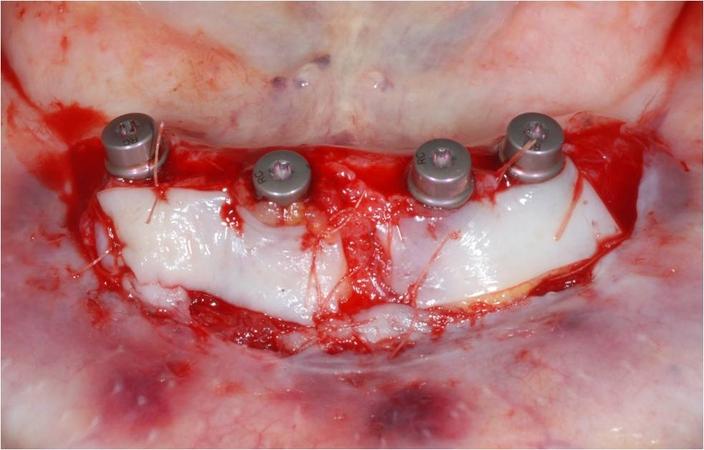
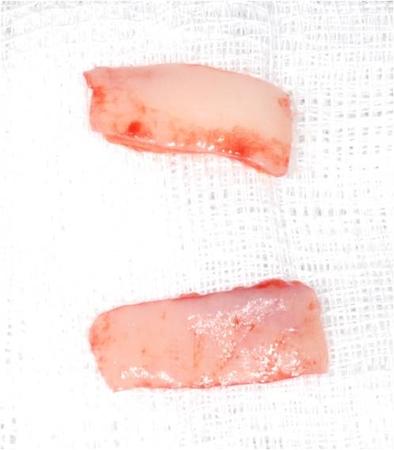
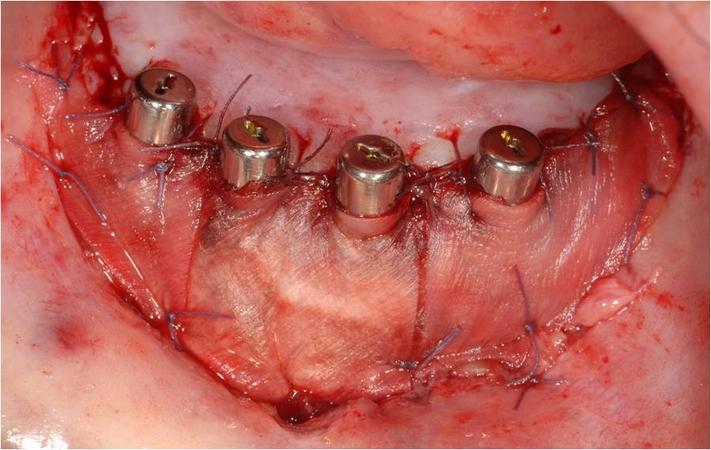
根据软组织缺损程度及其位置,使用不同技术和组织在穿粘膜种植体周围生成足够大的一片角质化粘膜。传统上使用自由软组织移植物进行再生。当需要角质化牙龈时,取自上鄂和磨牙后垫的自由牙龈移植物是目前针对种植体周围小区域的标准再生技术(图 2)。由于可用性和发病率的原因,自由牙龈移植物的使用受到限制(移植物尺寸:10 x 30 mm)。最近,种植体周围软组织重建中引入了动物源性移植材料(例如猪胶原蛋白基质)(图 3)。
为了满足修复需求(例如固定全口义齿或为覆盖义齿的凸缘提供空间),可能需要进行前庭加深。前庭加深有在数年后快速减少的趋势。前庭加深与基于种植体的疗法相结合似乎是最佳选项。
种植体周围软组织处理的成功与限制
成功取决于重建的软组织的萎缩情况。在研究中,动物源性的基质显示出了与自由牙龈移植物相似的临床效果。关于增加角质化/附着牙龈的宽度和厚度,哪种是理想移植物以及哪种是最佳技术,可供建议的信息并不多。