-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
辅助夹板固定
Key points
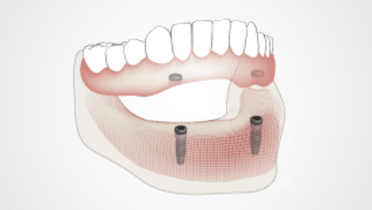
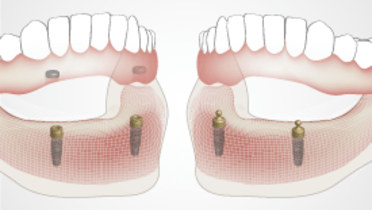
- 附着体直接放置在种植体上,因为球形附着体或定位器能够对覆盖义齿起到充分的固定作用,但一段时间后往往会失去固定性
- 与杆卡固定相比,粘膜炎发生率较低
- 套筒冠引起的技术性并发症发生率似乎较低
- 所有在两个种植体上放置覆盖义齿的设计都起到铰接覆盖义齿的作用,导致经常需要进行重衬
- 覆盖义齿比固定牙桥需要更多的维护工作
优点
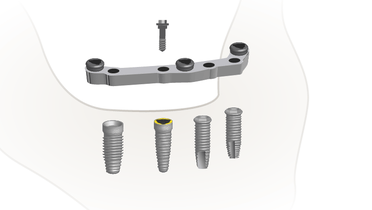
将固定附着体直接放置在种植体上的优点是,大多数凹组件都可插入预先存在的义齿,从而提供一种节约成本的治疗方案。由于此类附着体没有主要夹板固定,因此更易于清洁,种植体周围软组织状况优于使用杆卡的主要夹板固定情形。
局限性
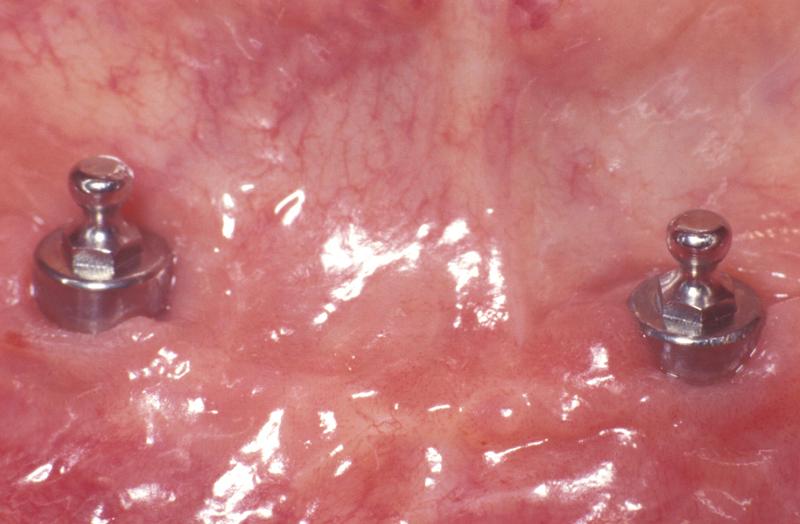
球形附着体至少需要 6 毫米的垂直空间,使用螺丝刀可能会激活某些系统(例如 Nobel Biocare)中凹组件的固位力。
定位器只需要 2.9 毫米的垂直空间,这在咬合面间距离较小/牙弓较窄的病例中较为有利。使用不同的插入件时,固位力可能有所不同,从 ± 400 克到 > 2 千克不等。
套筒冠包括用螺丝固定到种植体上的主要内冠和连接到修复体上并安装在主要内冠上的辅助内冠。修复体通过主要内冠与辅助内冠之间的摩擦力固定。发生技术性并发症的频率似乎低于使用球形附着体或定位器的情况。另一方面,口腔修复的复杂性更高,大多数情况下都不可能利用现有义齿。
缺点
有证据表明,球形附着体和定位器的固位力随着时间的推移而大幅降低。有些研究报道,有必要在使用后的一年内更换定位器插入件。
覆盖义齿的维护工作量大于固定牙桥的维护工作量。其中包括基质维护,如活化搭扣或更换定位器插入件。所有在两个种植体上放置覆盖义齿的设计都起到铰接覆盖义齿的作用,导致需要在大多数修复体中进行重衬。
所有覆盖义齿设计的患者满意度都相似,但杆卡固定的覆盖义齿固位力较高,修复体并发症较少。单个附着体易于清洁的特点似乎弥补了其他缺点。
附着体类型对植入成功/失败似乎并无作用。