-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
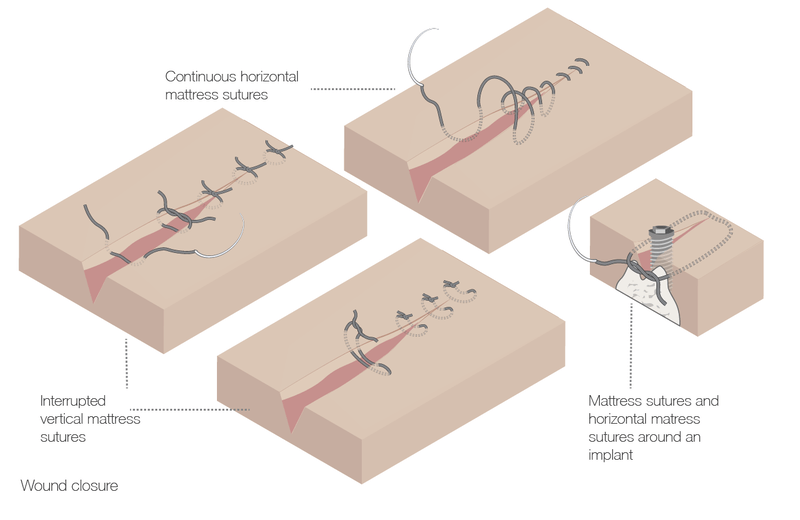
伤口闭合
Key points
- 温和地处理组织是确保无瘢痕愈合的关键
- 当预计存在创面张力时应采用褥式缝合法
- 单丝缝线不容易引起粘膜炎症,但会降低患者的舒适度
注意事项
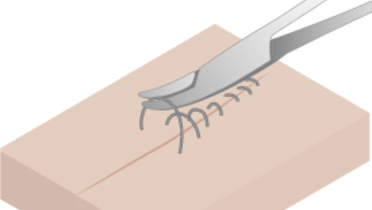
伤口闭合可保护手术部位并影响肉芽组织上角化细胞的迁移,从而确保并加速伤口愈合。一些伤口外翻可最大限度提高表皮对合。最常用的缝合类型是方结缝合,即在一个方向打两个结,然后在相反方向打第三个结。通常,间断缝合可比连续缝合提供更高的抗张强度。
方法概述
- 使用反三角缝合针可降低组织拖出缝线的风险
- 垂直穿透粘膜,即与粘膜呈 90° 角
- 在出口处用无齿镊固定缝针,然后将其从持针钳松开
- 温和的处理可避免组织缺血
- 缝线应在 7-14 天后拆除,具体取决于伤口长度、张力和患者的年龄
- 如果在褥式缝合时具有很高的粘膜张力,则宜延期拆除缝线
- 女性的口腔粘膜愈合时间长于男性
- 埋入的可吸收缝线可以留在原处
缝合和粘合材料
- 肠线不应再继续使用,目前已被性能更好的合成材料所代替
- 聚乙醇酸 (PGA) 缝线不受低 pH 值的影响。合成缝线通过水解作用去除,这是炎症反应引起的自然结果
- 丝线比合成材料价格便宜
- 复丝缝线有利于细菌迁移到组织
- 复丝替代品:聚乙烯、涤纶、聚丙烯或膨体聚四氟乙烯 (e-PTFE)。这些替代品更加坚固,可以降低所引起的炎症反应,但患者的舒适度较低
- 氰基丙烯酸酯粘合剂可能宜用于覆盖粘膜性供体部位
- 基于纤维蛋白的粘合剂在口腔手术中已不再具有任何适应证