-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
类固醇
Key points
- 大多数类固醇药物都是调节代谢和免疫功能的糖皮质激素
- 类固醇形成增多或长期服用会导致骨质疏松症状
- 尚无证据表明类固醇治疗与种植体治疗成功之间的联系
类固醇
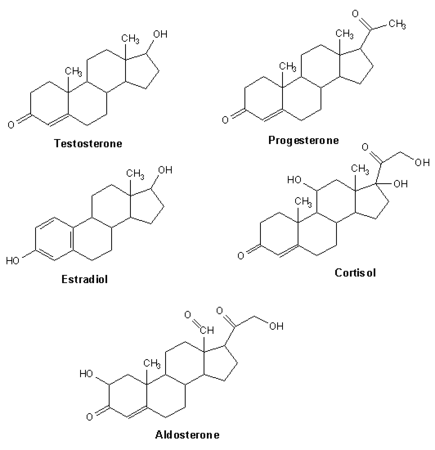
类固醇是一种有机化合物和脂质物质。类固醇在代谢中具有重要的作用,如膳食脂肪胆固醇、胆汁酸或类固醇激素(如肾上腺皮质酮/糖皮质激素、雌激素、睾酮)。由胆固醇可合成更复杂的类固醇(如类固醇激素或胆汁酸)。类固醇也是某些维生素(如维生素 D)和抑制剂(如洋地黄)的一部分。
一般医疗意义
类固醇不足是由于相关酶缺乏或机能不良而导致的,从而引发遗传疾病或肾上腺病理。这些腺体的皮质会产生类皮质激素。这些类皮质激素如果不足,可导致严重的代谢和荷尔蒙机能不良。如果不进行治疗,很多中年以上(女性)患者就会缺乏性类固醇激素并出现相关症状(骨质疏松症)。多数类固醇药物是皮质类固醇(糖皮质激素/肾上腺皮质酮或盐皮质激素/醛固酮)。肾上腺皮质酮形成增多或长期服用可能引发骨质疏松症(由于肠道钙吸收减少)和糖尿病(请参阅相关章节)。如果缺乏类固醇,或者患有各种免疫疾病和炎症(湿疹、神经性皮炎、扁平苔癣、风湿性疾病、银屑病)、慢性肠道疾病(克罗恩氏病、溃疡性结肠炎)、哮喘等,应给用类固醇药物(如强的松、氢化波尼松),器官移植和化疗后也可将其作为辅助用药。
通过全面了解既往病历/病史,可以确定在实施治疗前是否需要咨询内科医生/家庭医生。
种植体治疗的意义
患者长期接受类固醇疗法可能出现骨质疏松症症状。尚无证据表明骨质疏松症对口腔种植体成活率有影响。应考虑整骨治疗对于骨质疏松患者的影响。
在治疗方案设计阶段,应考虑借助现有技术对骨质和骨密度进行全面评估(请参阅有关临床评估/影像工具的章节)。在临床程序中准备对骨密度进行重新评估。充分调整临床方案;考虑具体(小尺寸)牙钻方案,为较松骨质选择合适的种植体。
长期摄入类固醇可增加感染的发生率。与抗炎止痛药(如布洛芬)联用会增加胃或十二指肠溃疡的风险。
如果需要大规模手术,患有阿狄森氏病的患者可能需要接受类固醇治疗,以降低患肾上腺危象的风险。后者是在由紧张压力所导致的皮质醇缺乏引起的。