-
0
Patient Assessment
- 0.1 Patient demand
- 0.2 Overarching considerations
- 0.3 Local history
- 0.4 Anatomical location
- 0.5 General patient history
-
0.6
Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.1 Risk assessment & special high risk categories
- 5.2 age
- 5.3 Compliance
- 5.4 Smoking
- 5.5 Drug abuse
- 5.6 Recreational drugs and alcohol abuse
- 5.7 Parafunctions
- 5.8 Diabetes
- 5.9 Osteoporosis
- 5.10 Coagulation disorders and anticoagulant therapy
- 5.11 Steroids
- 5.12 Bisphosphonates
- 5.13 BRONJ / ARONJ
- 5.14 Radiotherapy
- 5.15 Risk factors
-
1
Diagnostics
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
- 0.1 Lip line
- 0.2 Mouth opening
- 0.3 Vertical dimension
- 0.4 Maxillo-mandibular relationship
- 0.5 TMD
- 0.6 Existing prosthesis
- 0.7 Muco-gingival junction
- 0.8 Hyposalivation and Xerostomia
- 1.2 Clinical findings
-
1.3
Clinical diagnostic assessments
- 2.1 Microbiology
- 2.2 Salivary output
-
1.4
Diagnostic imaging
- 3.1 Imaging overview
- 3.2 Intraoral radiographs
- 3.3 Panoramic
- 3.4 CBCT
- 3.5 CT
- 1.5 Diagnostic prosthodontic guides
-
1.1
Clinical Assessment
-
2
Treatment Options
- 2.1 Mucosally-supported
-
2.2
Implant-retained/supported, general
- 1.1 Prosthodontic options overview
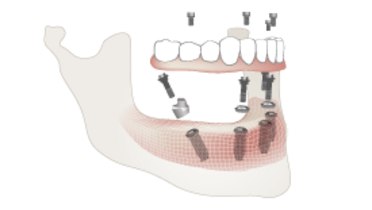
- 1.2 Number of implants maxilla and mandible
- 1.3 Time to function
- 1.4 Submerged or non-submerged
- 1.5 Soft tissue management
- 1.6 Hard tissue management, mandible
- 1.7 Hard tissue management, maxilla
- 1.8 Need for grafting
- 1.9 Healed vs fresh extraction socket
- 1.10 Digital treatment planning protocols
- 2.3 Implant prosthetics - removable
-
2.4
Implant prosthetics - fixed
- 2.5 Comprehensive treatment concepts
-
3
Treatment Procedures
-
3.1
Surgical
-
3.2
Removable prosthetics
-
3.3
Fixed prosthetics
-
3.1
Surgical
- 4 Aftercare
用陶瓷饰面
Key points
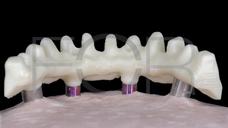
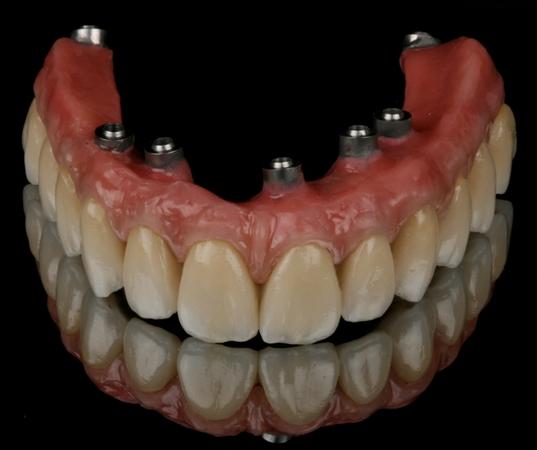
- 在骨吸收极少的情况下,优先选择陶瓷金属修复体以适应颌间空间限制
- 陶瓷饰面提供最佳美观效果和耐磨性并便于保持口腔卫生
- 为了最大限度地降低碎裂风险,适当设计框架的解剖结构以实现适当的陶瓷厚度非常重要
指南
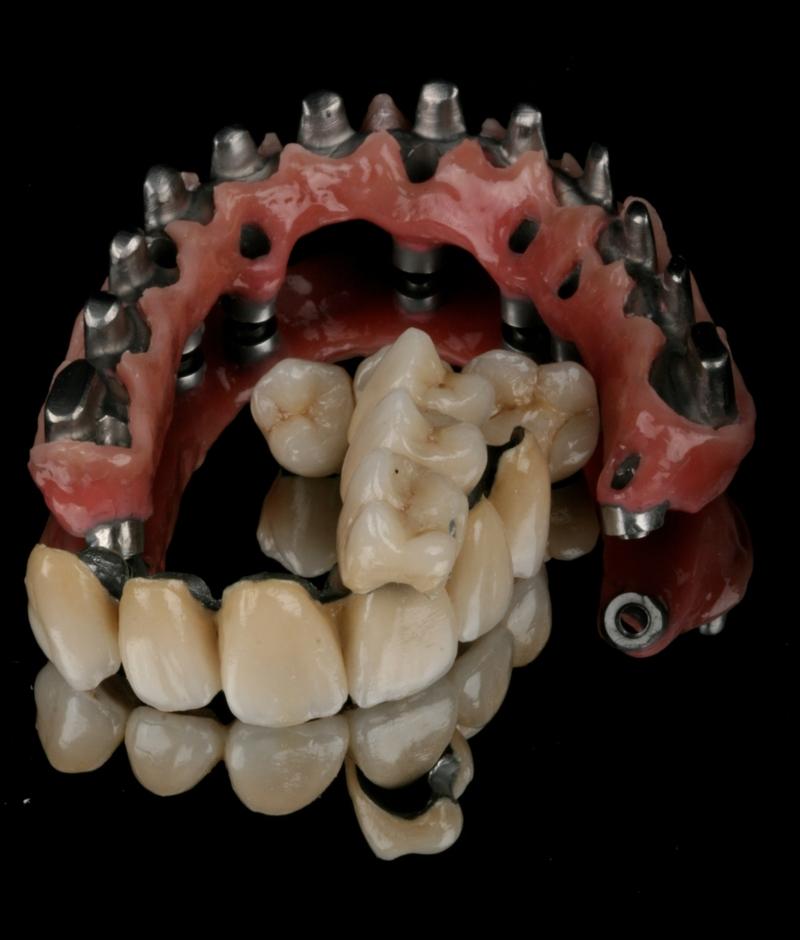
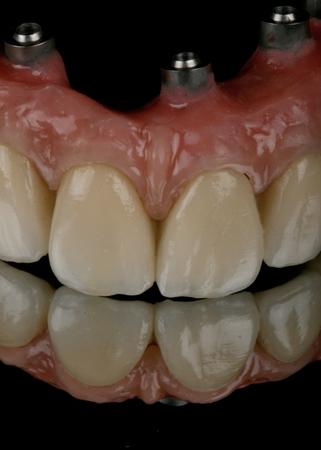
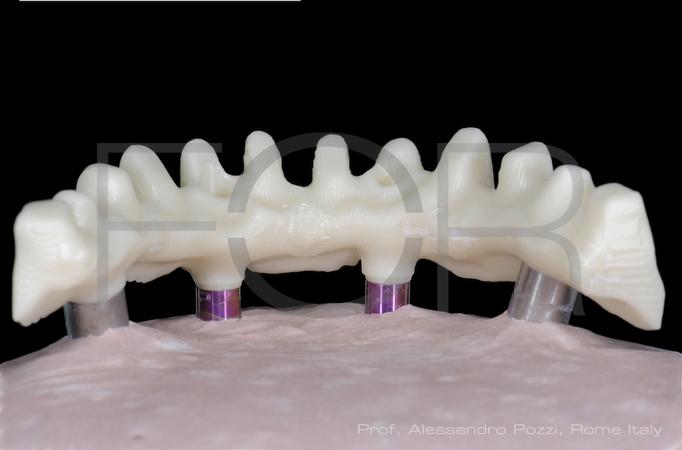
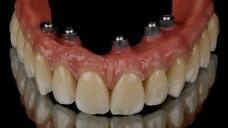
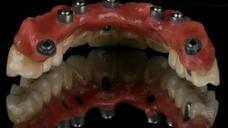
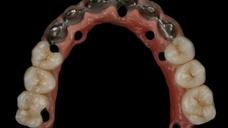
为了获得稳定的饰面陶瓷和理想的框架支撑,框架设计和形状应模仿最终修复体的设计,以便使陶瓷饰面层具有均匀的厚度。为了提供充分的美观饰面选项,组件选择和框架解剖结构设计应考虑 1.2 - 1.5 mm 的饰面厚度。高度抛光/上釉的表面至关重要,尤其是朝向粘膜的表面。
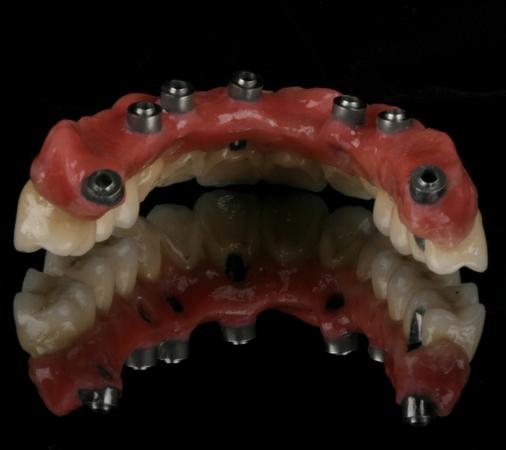
在使用螺丝固位修复体的情况下,螺丝通道孔将会穿过框架结构和饰面层。根据螺丝通道孔的位置和设计,在安放修复体后,封闭通道孔以避免食物嵌塞和损坏可能会有好处。通道孔通常采用光固化复合材料进行封闭。为了在将旋转工具穿过通道对修复体进行维护时便于取出复合物并保护螺丝,将复合物放置在一个软层上,例如特氟龙胶带、杜仲橡胶或棉球。
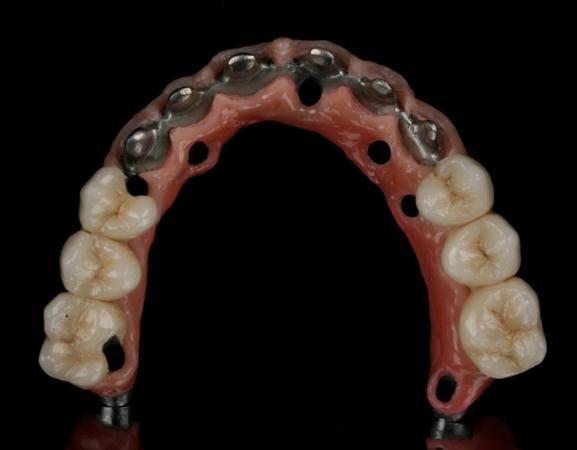
潜在并发症方面
氧化锆与饰面陶瓷之间的粘结机制目前尚不清楚,而且框架-饰面陶瓷接触面是这些修复体最脆弱的方面,因此可能会发生碎裂,这是潜在和最常见的并发症。对框架解剖结构进行适当设计以便具有适当的陶瓷厚度非常重要。已经开发了多种技术来解决陶瓷层可能碎裂的问题,例如“过度压接技术”,这种技术可提高分层材料的同质性和密度。可以将其视为不对咬合面进行贴面,而是保持氧化锆表面。在发生碎裂的情况下,螺丝固位修复体的易于取回性是一大优点。
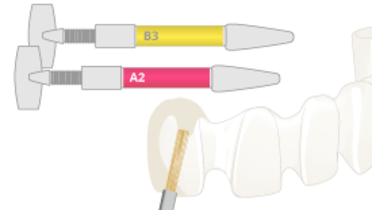
在使用旋转工具进行口腔内调整后,对陶瓷表面进行抛光至关重要,这可以提高患者舒适性并降低因切割陶瓷表面的不规则性导致出现裂纹的风险。在进行此类调整之后,甚至建议再次在技工室对陶瓷修复体表面上釉。
在口腔内长时间(数个月)使用后,由于饰面陶瓷在口腔内环境中的转换效应,成功更换并重烧陶瓷的技术可能性非常低。因此,在植入修复体后,应尽快确定并执行需要的任何调整。