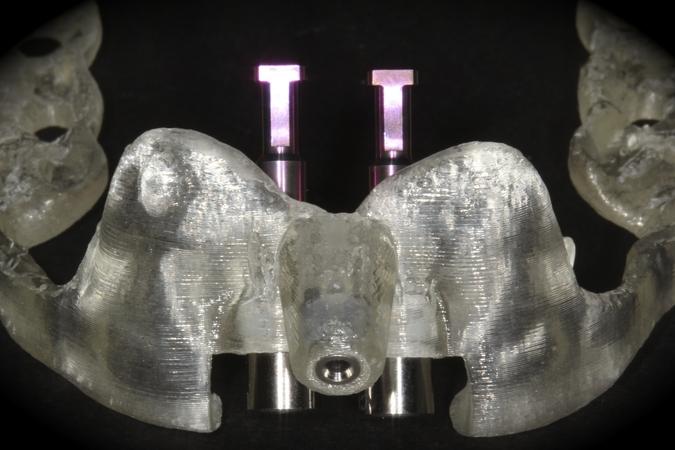
Extraction and replacement of maxillary central incisors
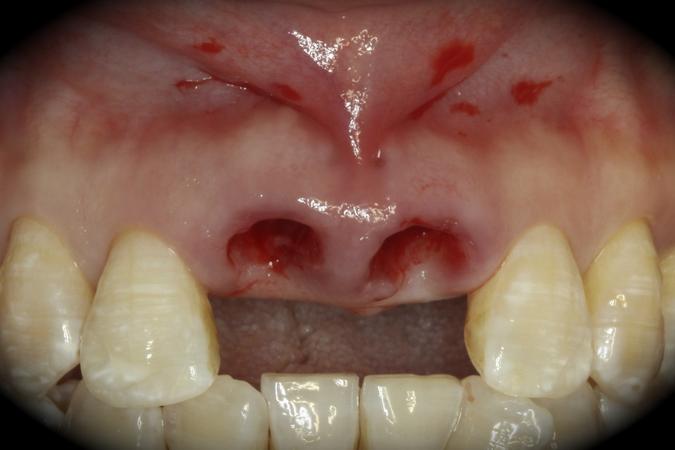
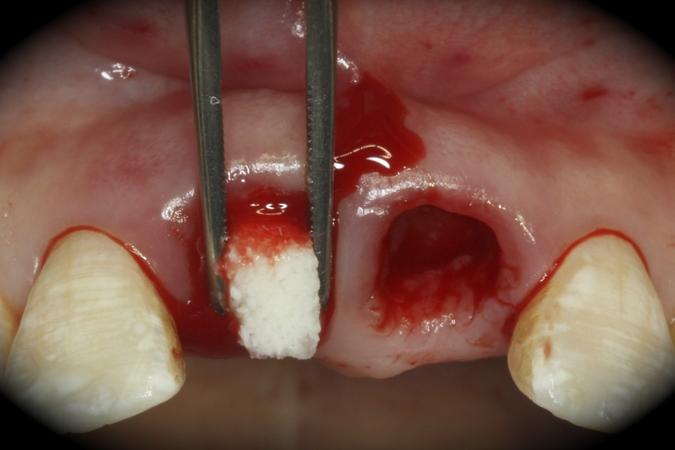
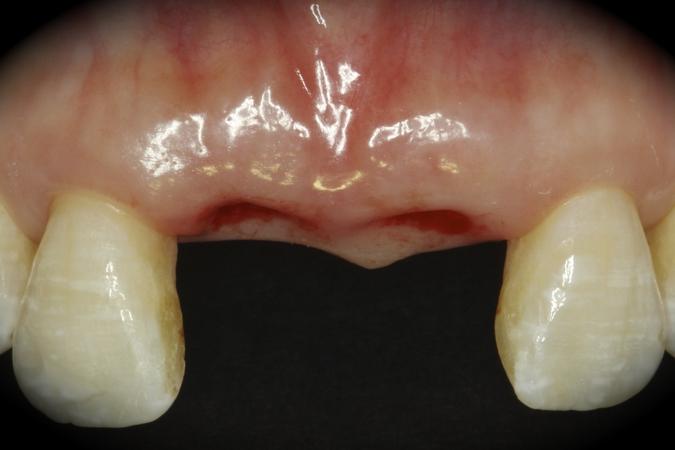
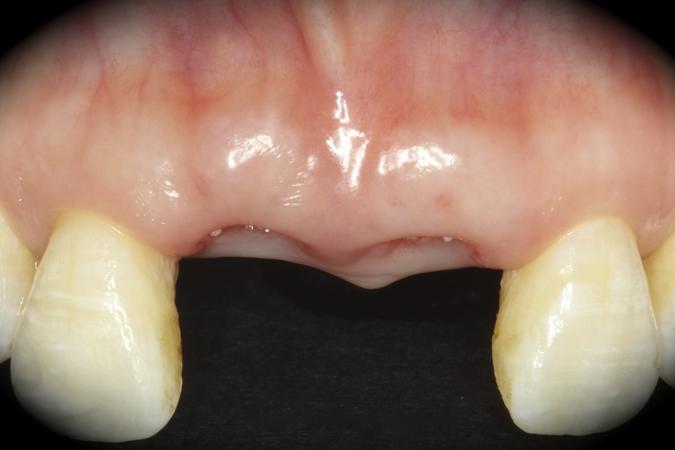
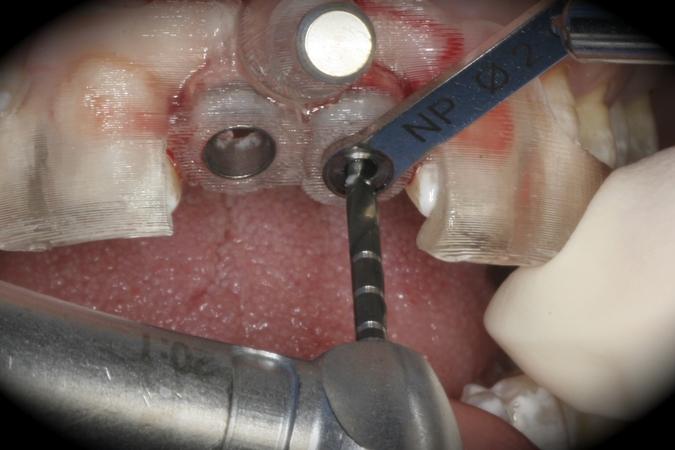
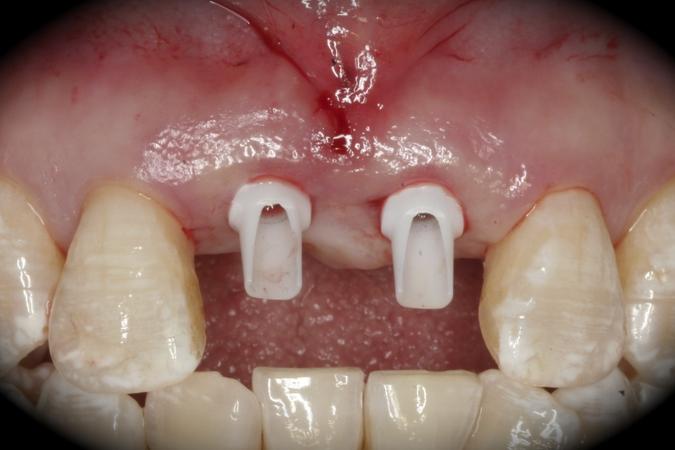
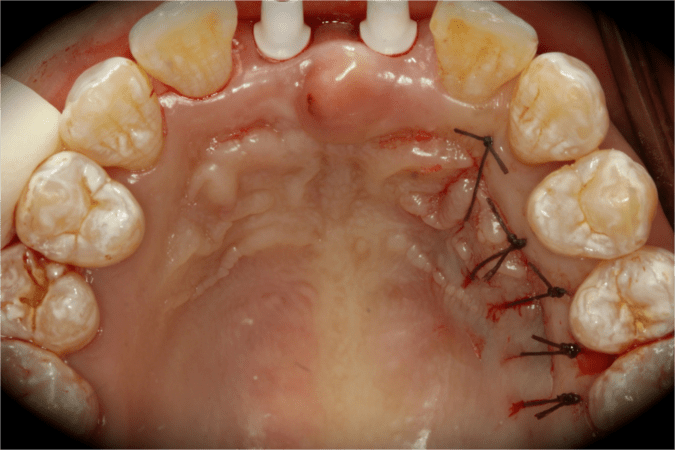
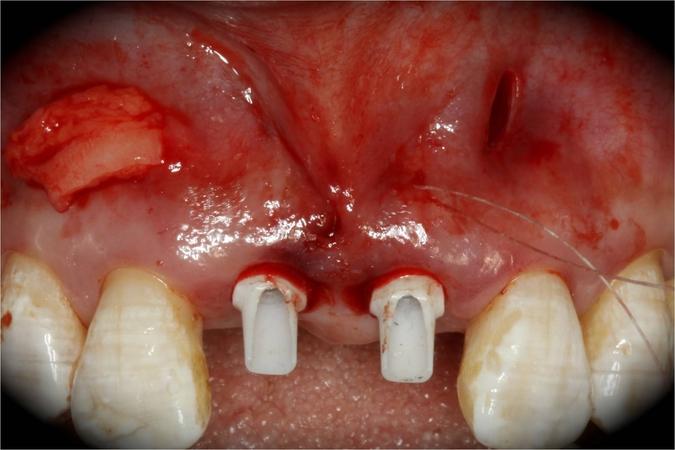
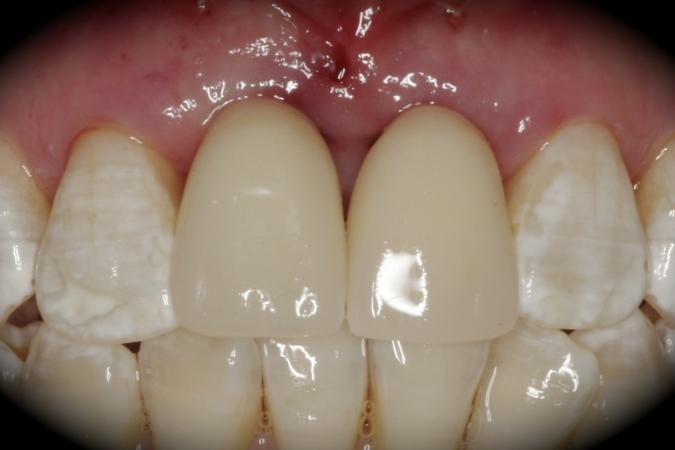
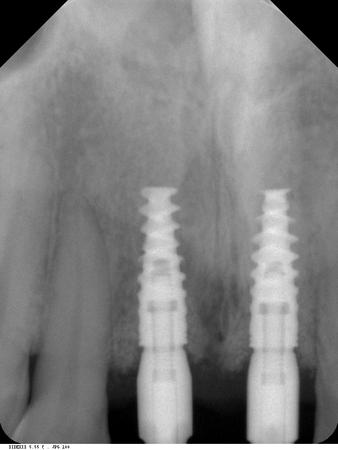
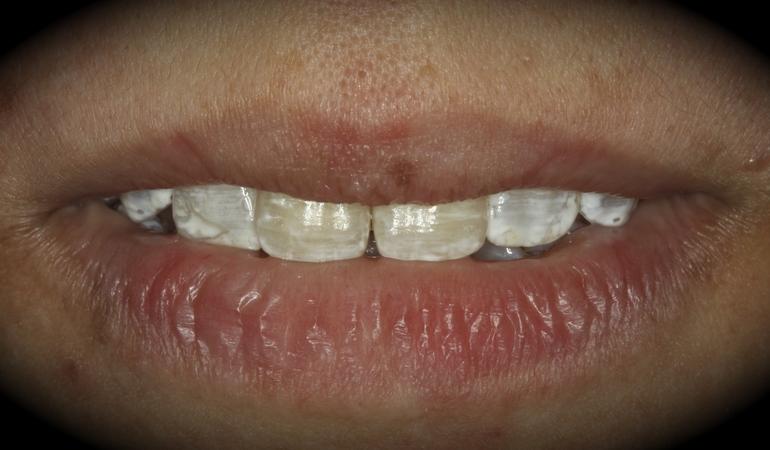
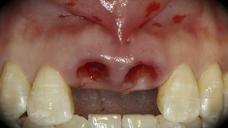
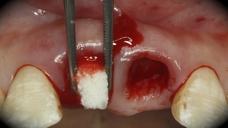
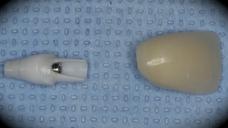
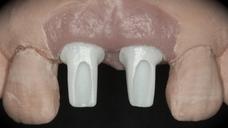
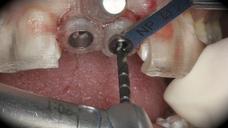
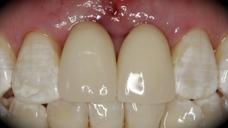
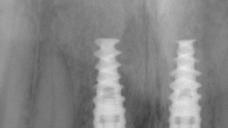
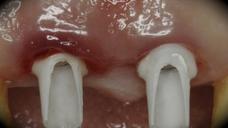
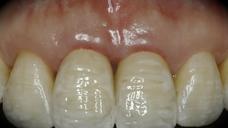
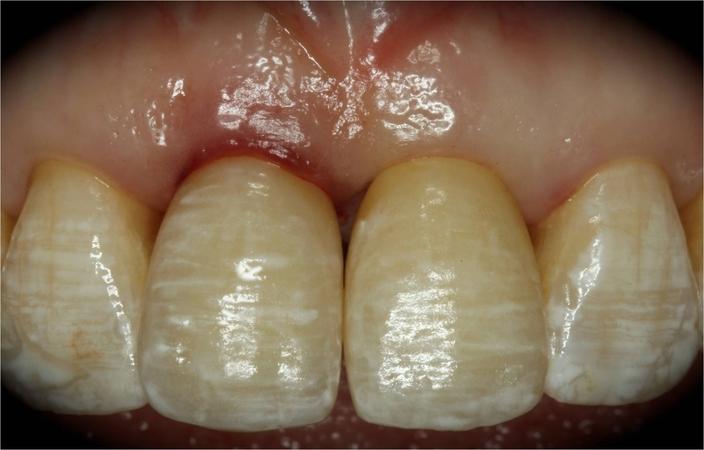
This patient is a young patient asking for dental implants to replace her hopeless maxillary central incisors. The patient's chief complaint was the increased mobility of her maxillary central incisors. She has a history of traumatic injury to the central incisors. They have been restored with crowns after the initial injury. She does not have any remarkable medical history, doesn't smoke or drink and she is classified as ASA I. Two adjacent implants in the aesthetic zone is considered a complex indication. There are additional aesthetic risks in this patient’s situation: 1. Gummy smile 2. Dental fluorosis 3. High expectation In view of the complexity of this case, a staged approach was employed which included: 1. Ridge preservation after extraction 2. Guided flapless surgery for implant placement 3. Simultaneous ridge augmentation with sub-epithelial connective tissue graft 4. Immediate provisional restorations to support the peri-implant soft tissue 5. Custom design of ceramic abutments and crowns to enhance the white and pink aesthetics. The salient points in the management of this case are: 1. CBCT examination was conducted to allow accurate diagnosis and planning for guided surgery; 2. Computer-based planning was used to illustrate to patient the important aspects of her situation; 3. Ridge preservation was performed to reduce shrinkage after extraction; 4. A flapless procedure was performed to minimize surgical trauma to the soft tissue; 5. NobelActive™ implants were chosen for the advantages of good initial stability and platform-shift design; 6. Sub-epithelial connective tissue graft was used to further improve the volume of the soft tissue; 7. Immediate provisional restorations were given to the patient for function and aesthetics; 8. Definitive restorations were designed and manufactured by the Procera™ CAD/CAM process as an individualized solution; 9. Zirconia abutments and crowns were modified and characterized by our in-house laboratory technician to achieve satisfactory aesthetic outcome; 10. Regular maintenance was scheduled to ensure good oral health status including the natural dentition and implants. Conclusion: Following a carefully implemented staged approach, adjacent single-tooth implant restorations for the maxillary central incisors are effective and successful. This patient is happy with the functional and aesthetic outcomes.