Multi-disciplinary treatment of absent central incisors
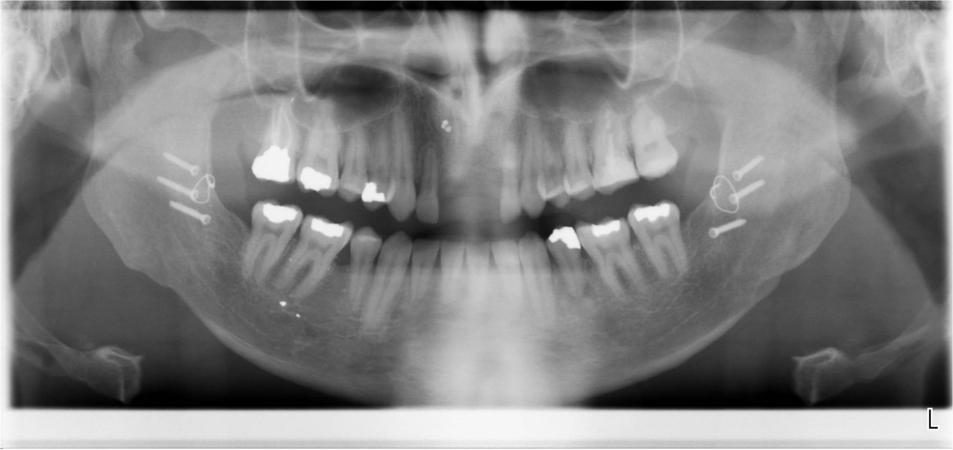
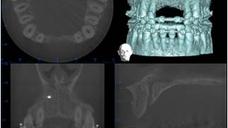
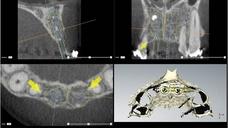
This patient presented after a bilateral sagittal split osteotomy performed to correct a Class II deep bite. During the same surgery, an autogenous chin graft was placed in order to augment the anterior maxilla. The bone graft caused a fenestration of the soft tissue and the fixation screws became clearly visible. The patient was then referred for further complication management and implant treatment. The initial approach was to remove the fixation screws and debride the bone graft very conservatively in order for the epithelium to granulate and cover the graft. Once this was achieved, further treatment planning and treatment could be started.
Detailed treatment history:
1. Assessment: The patient was a take-over case. He was thus re-evaluated by an orthodontist, MFOS and prosthodontist.
2. Primary objective: To establish a healed bone site with no fenestration of bone into the oral cavity. This could be achieved over a period of several weeks where the screws were removed and the bone was gently reduced under local anesthesia. Meticulous attention was given to the oral hygiene of the patient. Finally, a sufficient thickness of soft tissue was gained to cover the bone. The subsequent steps could then be initiated. A surgical stent was fabricated by the prosthodontist and lab technician.
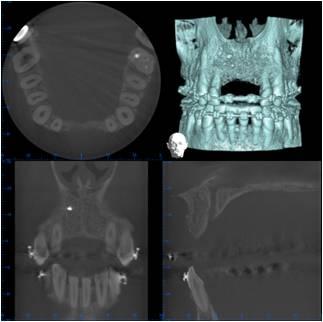
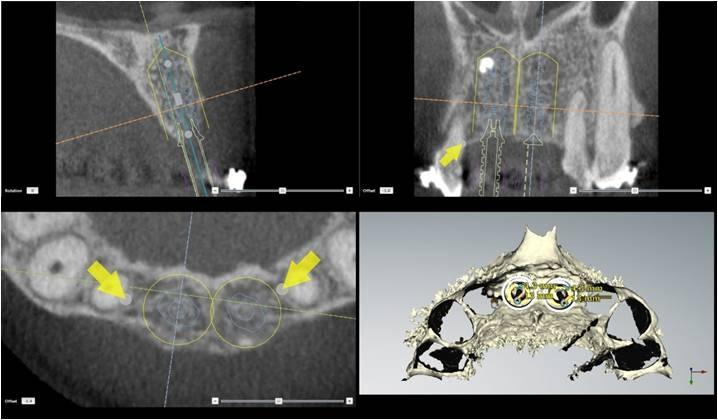
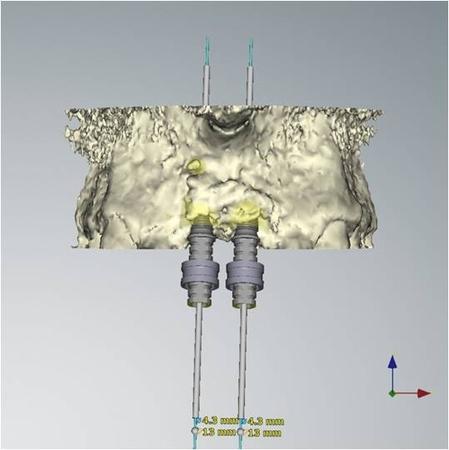
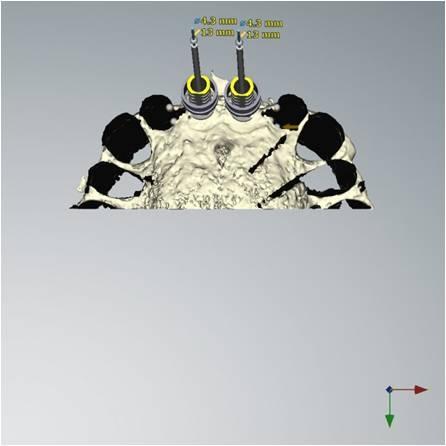
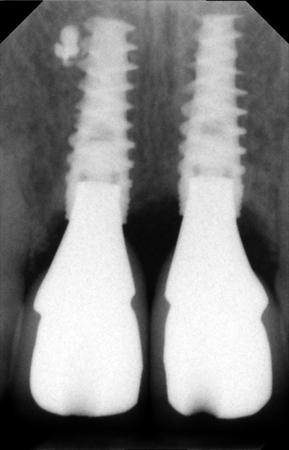
3. Surgery: The patient was treated under conscious sedation. A full thickness flap was elevated, extending distally of the premolars. The flap was reflected at the level of the nasal spine. A ridge split was done - the alveolar bone was mostly broad enough to allow for implant placement - but unfortunately, this bone was located too far to the palate. The most apical bone, however, was strong enough to hold the NobelActive implants. The apical aggressive thread of the implant ensured a good primary stability. Additional grafting was done with autogenous bone from the pterygoid region and BioOss was added for 3D bulk. The soft tissue had to be released and the first priority was to close the broadened alveolar ridge carrying the dental implants. As a temporary prosthetic solution, two resin crowns were bonded to the two lateral incisors. Soft tissue profiling could be achieved with this temporary prosthesis.